Figure 1.
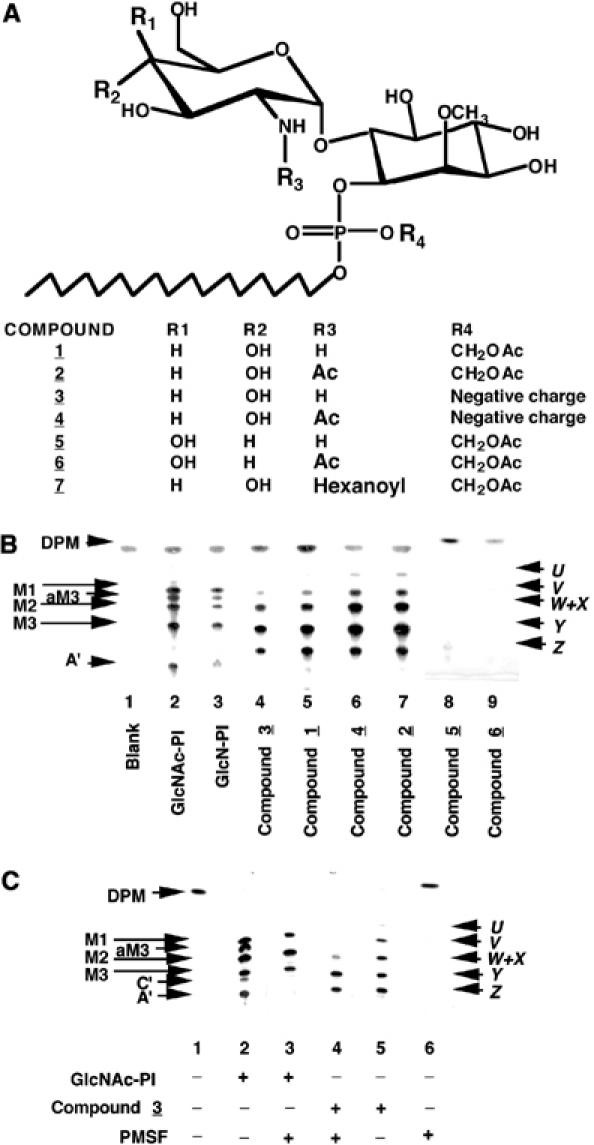
Novel analogues of GlcN-PI and their metabolism by a trypanosome cell-free system. (A) Structures of the synthetic GlcN-PI analogues used in this study. (B) Synthetic GlcNAc-PI and GlcN-PI (positive controls, lanes 2 and 3) and analogues thereof (compounds 1–6, lanes 4–9) were incubated with a modified trypanosome cell-free system and GDP-[3H]Man. Radiolabelled glycolipid products were analysed by HPTLC and fluorography. The products were characterized by enzymatic and chemical digestions (Table I) and are: DPM, dolichol-P-mannose; M1-3, Man1–3GlcNα1-6PI; aM3, Man3GlcNα1-6(2-O-acyl)PI; A′, EtNP-Man3GlcNα1-6PI; C′, EtNP-Man3GlcNα1-6(2-O-acyl)PI; X–Z, Man1–3GlcNα1-6(2-O-methyl)D-myo-inositol1-P-octadecanol; U–W, Man1–3GlcNα1-6(2-O-methyl) (?-O-acyl)D-myo-inositol1-P-octadecanol. (C) Synthetic GlcNAc-PI (control, lanes 2 and 3) and compound 3 were incubated with the trypanosome cell-free system in the presence (+) and absence (−) of PMSF. Radiolabelled glycolipid products were analysed by HPTLC and fluorography.
