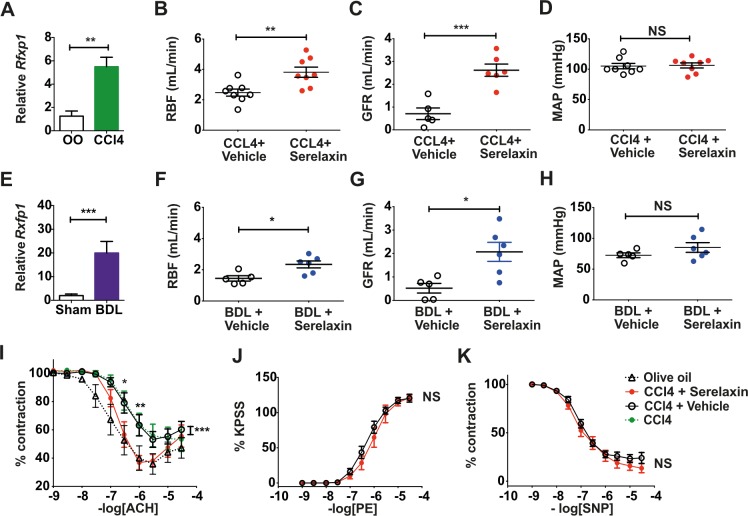
Fig 3. Effect of 72-h serelaxin infusion on renal perfusion and renovascular responses in cirrhotic rats.
Relative Rxfp1 transcripts (normalized to 18S rRNA) in whole kidney extracts from 16-wk CCl4 (A) and 4-wk bile duct ligation (BDL) (E) rats (n = 3–6). Renal blood flow (RBF; B and F), mean arterial pressure (MAP; D and H), and glomerular filtration rate (GFR; C and G) in CCl4 and BDL rats after 72-h s.c. serelaxin or vehicle (n = 5–8). Data presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM), analyzed by unpaired t-test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; NS, not significant). Concentration–response curves to acetylcholine (ACh; I), phenylephrine (PE; J), and sodium nitroprusside (SNP; K) in the presence of serelaxin or vehicle in 16-wk CCl4 rats (n = 5–8). Data presented as mean ± SEM, analyzed by two-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni correction (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). OO, olive oil.