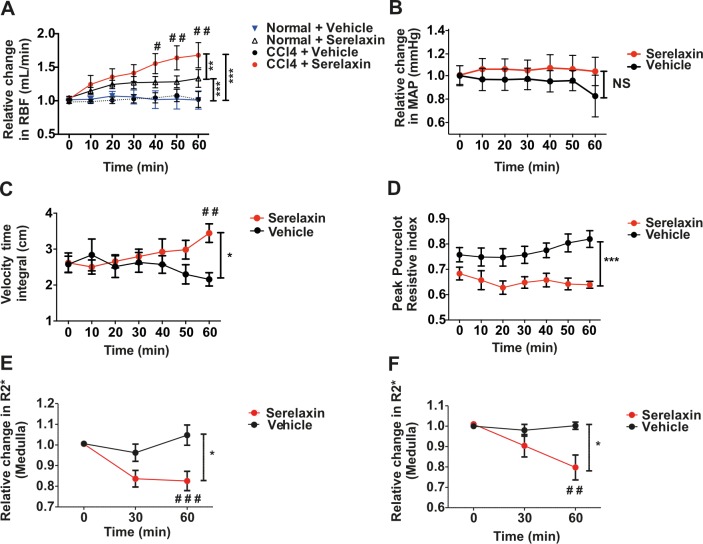
Fig 5. Effect of acute serelaxin treatment on renal blood flow and tissue oxygenation in CCl4 cirrhotic rats.
Renal blood flow (RBF, A) and mean arterial pressure (MAP, B) responses to acute i.v. serelaxin (4 μg) or vehicle in 16-wk CCl4 rats (n = 5–7). Measurement of velocity time integral (C) and renal resistive index (D) following acute i.v. serelaxin (4 μg) or vehicle (n = 6–8). Deoxygenated hemoglobin levels (R2*) in renal medulla in 8-wk (E) and 16-wk (F) CCl4 rats at baseline, 30 min, and 60 min following acute i.v. serelaxin (4 μg) or vehicle (n = 5–8). Data presented as mean ± standard error of the mean, analyzed by two-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; NS, not significant) with post hoc Bonferroni correction to compare individual CCl4 time points with respective vehicle controls (#p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.001).