Figure 7.
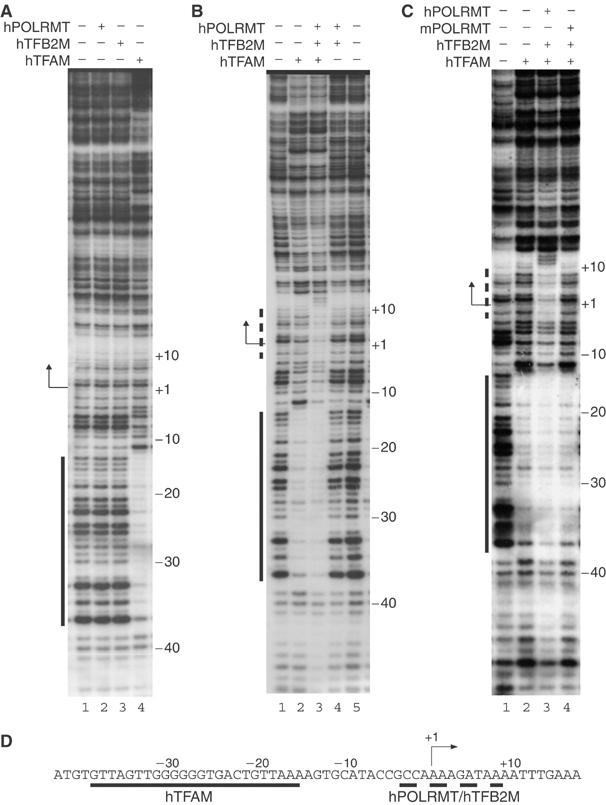
Promoter recognition by hPOLRMT/hTFB2M is strictly dependent on hTFAM (A). DNase I footprinting reveals that neither hPOLRMT nor hTFB2M (lanes 2 and 3) in isolation interacts with hLSP. The binding site for hTFAM (lane 4) is indicated with a solid line. (B) The hPOLRMT/hTFB2M heterodimer interacts with the transcription start site in the presence (lane 3), but not in the absence (lane 4), of hTFAM. The region protected by hPOLRMT/hTFB2M is indicated with a dashed line. (C) The hPOLRMT/hTFB2M complex (lane 3), but not the mPOLRMT/hTFB2M complex (lane 4), interacts with the hLSP transcription start site in the presence of hTFAM. (D) A schematic representation of protein interactions with hLSP. Human TFAM protects the −15 to −38 region (solid line) and the hPOLRMT/hTFB2M heterodimer protects the +10 to −4 region (dashed line).
