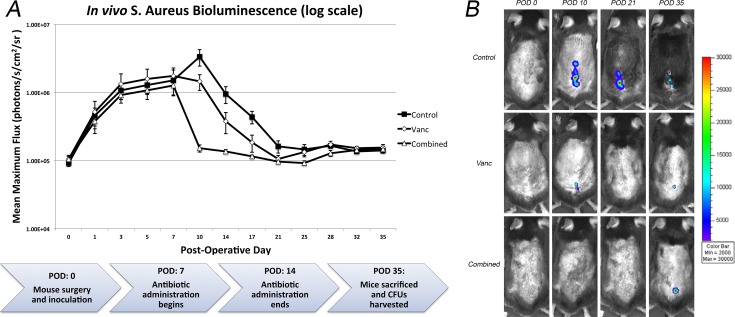
Fig 1. Measurement of bacterial burden using in vivo bioluminescence to POD 35.
1x103 CFU of S. aureus possessing the bioluminescent construct in a stable plasmid (Xen36) were inoculated into the L4 spinous process of mice (n = 10 mice per group) in the presence of a stainless steel implant. (A) Bacterial counts as measured by in vivo S. aureus bioluminescence (mean maximum flux [photons/s/cm2/sr] ± sem [logarithmic scale]), with a flow diagram of the experimental protocol below. On POD 7, antibiotic administration began with vancomycin, a combination of vancomycin and rifampin or a sterile saline control. Antibiotic administration was stopped on POD 14. On POD 35, mice were sacrificed and CFUs from the implant and surrounding tissue were measured. (B) Representative in vivo S. aureus bioluminescence on a color scale overlaid on top of a grayscale image of mice.