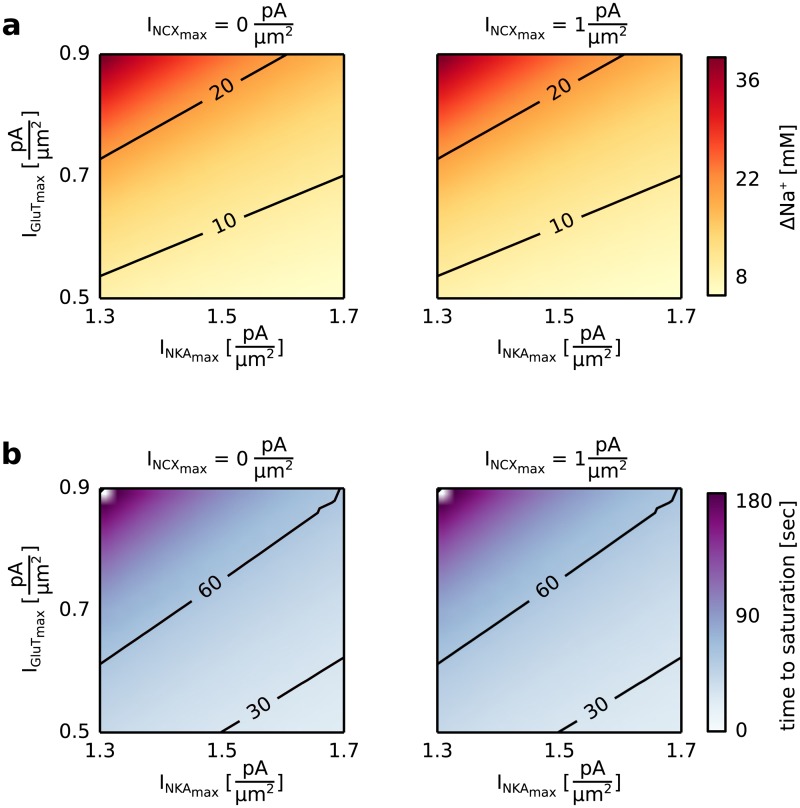
Fig 5. Increase of the Na+ concentration in the intracellular compartment, [Na+]i, during a constant extracellular glutamate concentration for different values of the maximal pump currents of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (INCXmax), the glutamate transporter (IGluTmax), the Na+/K+-ATPase (INKAmax).
The astrocytic compartment was stimulated for 200 seconds with a constant extracellular glutamate concentration of 100 μM. The surface volume ratio (SVR) was set equal to 1 μm-1, which corresponds to astrocytic compartments close to the soma. a [Na+]i after 200 seconds with respect to its resting concentration ([Na+]rest = 15 mM, Δ Na+ = [Na+]End—[Na+]rest) for a maximal pump current of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (INCXmax) equal to 0 (left) or equal to 1 (right) and different values of the maximal pump current of the glutamate transporter (IGluTmax) and the Na+/K+-ATPase (INKAmax). b Time to reach saturation for a maximal pump current of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (INCXmax) equal to 0 (left) or equal to 1 (right) and different values of the maximal pump current of the glutamate transporter (IGluTmax) and the Na+/K+-ATPase (INKAmax). The time to saturation was defined as the time required for the intracellular Na+ concentration to remain on a constant concentration.