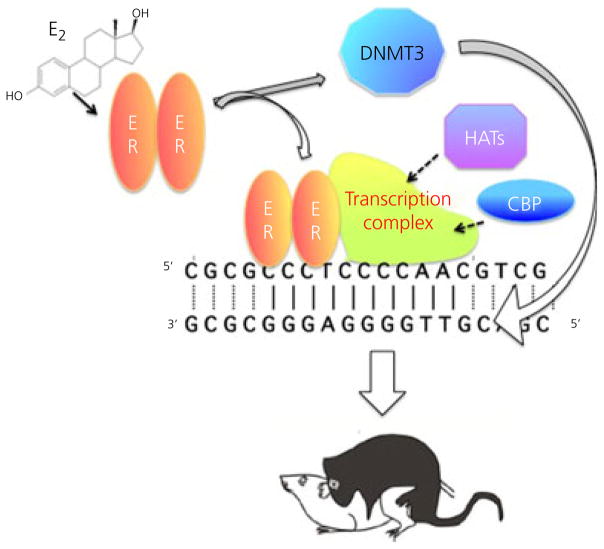
Fig. 3.
Epigenetics and sexual differentiation. Oestradiol (E2) binds to and activates its nuclear transcription factor receptor (ER) which moves to the DNA and recruits a transcriptional complex. Included in this complex are enzymes with histone-acetylating ability to allow access to the DNA. Activated ER may also modify the activity of DNA methyl transferase (DNMT) enzymes and thereby alter the methylation status of the DNA. Taken together, these changes may provide the molecular basis for the organisational effects of early hormone exposure, which endure into adulthood and direct activational responses to sex-typic gonadal steroids. CBP, CREB-binding protein; HATs, histone acetyl transferases.