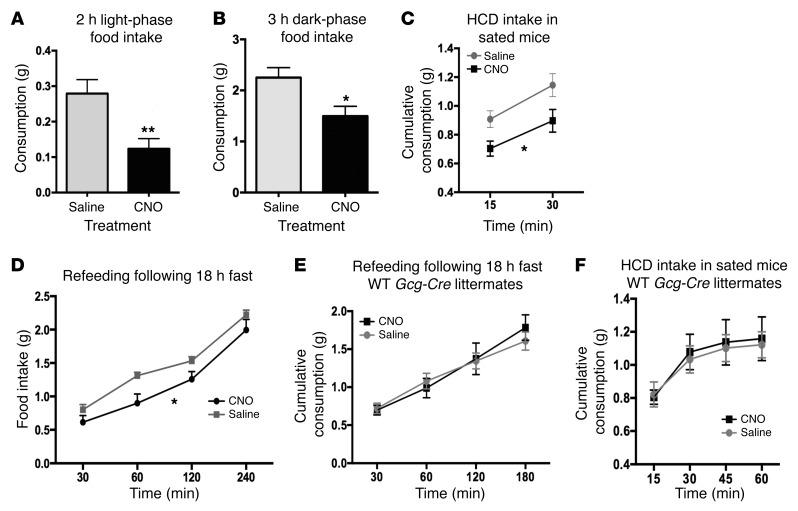
Figure 4. GCG neuron activation modulates food intake in both fed and fasted animals.
Activation of GCG neurons by CNO (2 mg/kg) reduced food intake both in the light phase (A, paired t test, n = 11, **P = 0.005) and during the first 3 hours of the dark phase (B, paired t test, n = 8, *P = 0.026) upon return of food 2 hours after i.p. CNO/saline injections. HCD intake during early daytime when mice were sated (following ad libitum overnight feeding on chow) was significantly reduced after CNO injection (C, 2-way repeated measures ANOVA, main effect of treatment F1,11 = 8.66, *P = 0.0134). Food intake during daytime refeeding following 18 hours of fasting was also significantly reduced (D, 2-way repeated measures ANOVA, n = 13, main effect of treatment, F1,12 = 5.118, *P = 0.0430). WT littermates that underwent sham brain surgery were tested by injection of either CNO (5 mg/kg) or saline i.p., and no effects of CNO were apparent during refeeding after fasting (E, 2-way repeated measures ANOVA, F1,5 = 0.06308, P = 0.8) or during HCD feeding (F, 2-way repeated measures ANOVA, F1,5 = 0.07558, P = 0.62).