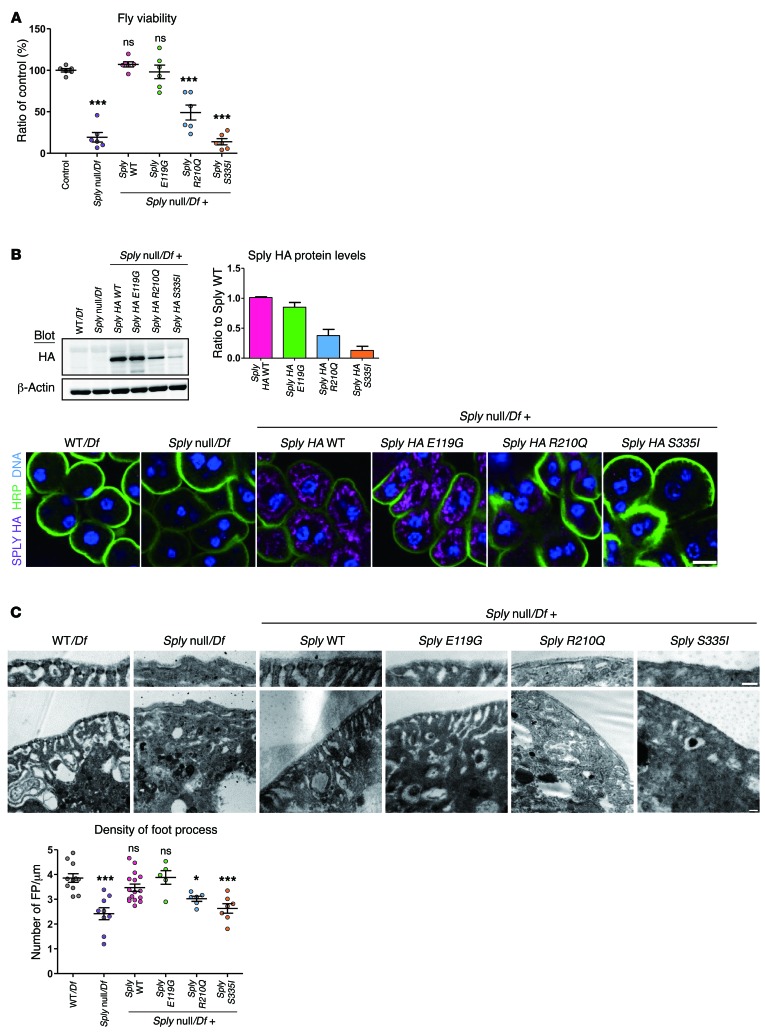
Figure 4. SGPL1 missense mutations fail to rescue the phenotype of the Drosophila SGPL1 ortholog (Sply) KO.
Human SGPL1 mutations p.Glu132Gly, p.Arg222Gln, and p.Ser346Ile are equivalent to Drosophila Sply mutations p.Glu119Gly, p.Arg210Gln, and p.Ser335Ile. (A) Viability defects of Sply null hemizygous and Sply mutant flies. Viability was calculated as the percentage of Sply null hemizygous offspring of heterozygous parents. Values are normalized to the viable control Df(2R)BSC433/Df(2R)247. More than 650 flies per genotype; 6 independent experiments. (B) Western blot of HA-tagged Sply in third instar larvae (top panel) and immunofluorescence of third instar garland nephrocytes stained for HA (purple) (bottom panel). Membrane and nuclei were labeled with HRP (green) and Hoechst (blue), respectively. Five or more larvae/genotype; 3 independent experiments. Scale bar: 10 μm. (C) Foot process density in Sply null hemizygous and Sply mutant third instar garland nephrocytes. TEM images and quantification. Six or more nephrocytes/genotype; 2 independent experiments. Scale bars: 200 nm. Statistical analysis performed by Bonferroni’s test following ANOVA. ***P < 0.0005; *P < 0.05. All graphs show mean ± SEM. ns, not significant.