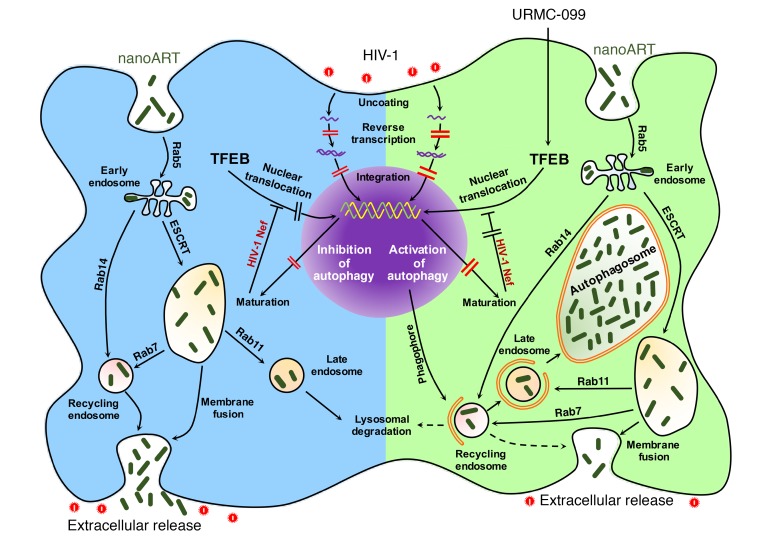
Figure 9. URMC-099 facilitates depots of nanoART in macrophage autophagosomes.
Nanoformulated ARVs enter the MDM via clathrin-coated pits and are transported to the early endosomes. Parts of the nanoARV are recycled by getting into recycling endosomes by Rab14-mediated fast recycling or trafficking regulated by endosomal sorting complexes required for transport machinery (ESCRT) and Rab7. The particles reach late endosomes via ESCRT and Rab11 and eventually fuse with lysosomes. HIV-1 fuses with the cell and releases its contents to the cytoplasm. Partial core shell uncoating and reverse transcription lead to the formation of a preintegration complex that enters the nucleus, and provirus is formed following integration. After proviral transcription and translation, viral assembly and maturation take place. HIV-1 Nef inhibits autophagy by sequestering TFEB in the cytoplasm. A subtherapeutic dose of nanoART limits antiretroviral responses. URMC-099–assisted nuclear translocation of TFEB overcomes HIV-1 Nef–mediated inhibition of autophagy. This affects autophagosome formation and retention of nanoformulated drugs specifically in the autophagosomes. In the presence of URMC-099, nanoformulated ARV retention is increased, and release is decreased even with a subtherapeutic drug dose, ultimately attenuating HIV-1 infection.