Figure 5.
Multi-neuron Conditioning
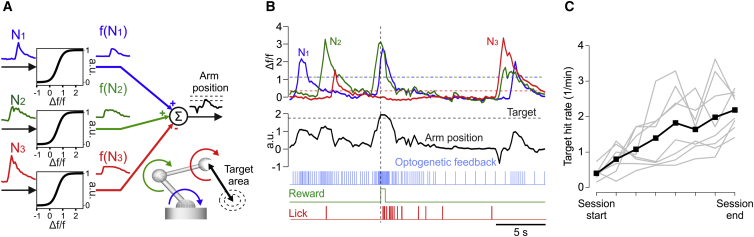
(A) The Δf/f0 activities N1, N2, and N3 of three CNs were first transformed by a logistic function (see STAR Methods) into f(N1), f(N2), and f(N3), and the ensemble activity computed by adding f(N1) and f(N2) and subtracting f(N3). Each activity transform dictated the angular position of a robotic actuator and the ensemble activity was proportional to the effector distance to target.
(B) Example Δf/f0 traces of the three simultaneously conditioned neurons, their ensemble activity computed as in (A), and its real-time transform into a rate signal of optical pulses encoding the distance to target.
(C) Mean and individual session (n = 8, two mice) target hit rates indicate that mice could learn the multi-neuron conditioning task under the guidance of optogenetic feedback.