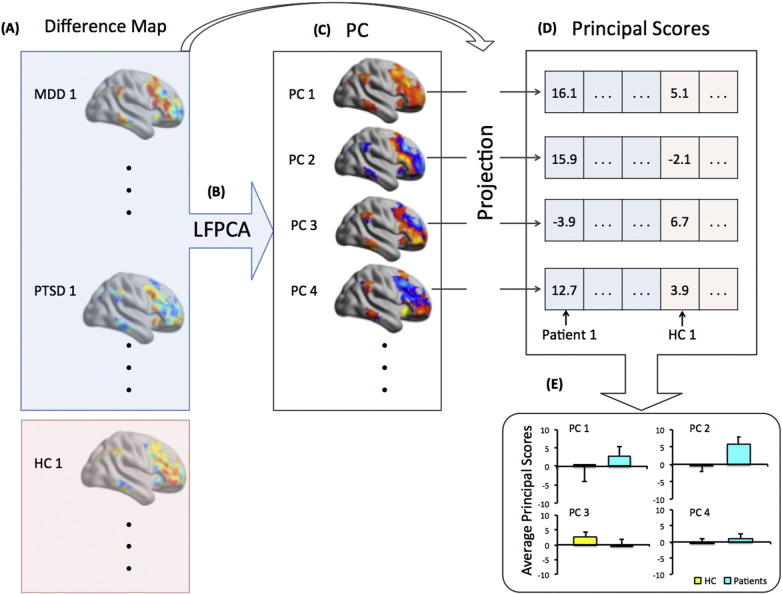
Fig. 1.
Procedures for Longitudinal Functional Principal Components Analysis (LFPCA). (A) For the set of 53 participants included in the analysis, calculate the difference maps of amygdala functional connectivity (Δ Amygdala FC) between time 2 and time 1 for each individual, within the fronto-parietal network as defined by Yeo et al. (Yeo et al., 2011). (B) Aggregate the data across all patients (18 MDD and 17 PTSD) and conduct singular value decomposition (SVD) within the fronto-parietal network. (C) Obtain the eigenimages in the Yeo fronto-parietal network template where the value of each voxel represents the loadings of the principal components (PC) within the fronto-parietal network. The color maps indicate the relative loadings that contribute to the corresponding principal component, with red for positive loadings and blue for negative loadings. Colors are based on the actual PCA results. Voxels with higher absolute values are regions that most reflect the longitudinal changes in amygdala connectivity. (D) Project each amygdala connectivity difference map (including patients and controls) onto the identified eigenimage and obtain a principal score for each subject and each eigenimage. (E) Perform statistical testing on the principal scores to identify the PC that best differentiates patients from healthy controls.