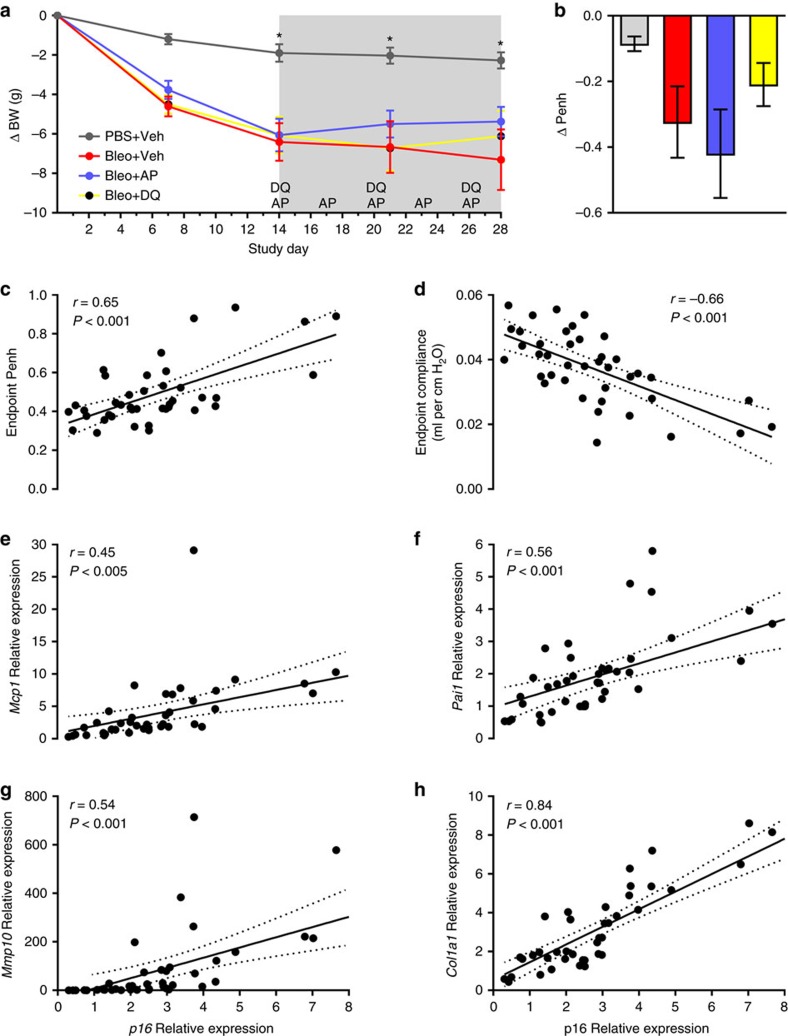
Figure 5. Retention of p16-positive cells impedes resolution of bleomycin lung injury.
(a) Ink-Attac transgenic mice receiving bleomycin (Bleo) through aerosolized intratracheal instillation were randomized to vehicle (Veh), AP or DQ and were compared with PBS-exposed, Veh-treated mice. Mice were treated as indicated from day 14–28 (grey shading). Body weight (BW) was monitored daily and is depicted as change in grams relative to baseline (*P<0.05). (b) Endpoint (4 weeks post exposure) Penh levels were compared to Penh levels measured at treatment randomization (2 weeks post exposure). Lung p16 expression levels measured by RT–PCR (normalized to Hprt) were compared with endpoint (c) Penh, (d) airway compliance, (e) Mcp1, (f) Pai1, (g) Mmp10 and (h) Col1a1 expression in bleomycin-injured mice (mean±s.e.m.; PBS+Veh n=6 (grey), Bleo+Veh n=13 (red), Bleo+AP n=15 (blue), Bleo+DQ n=14 (yellow). Pearson's correlation statistics are indicated).