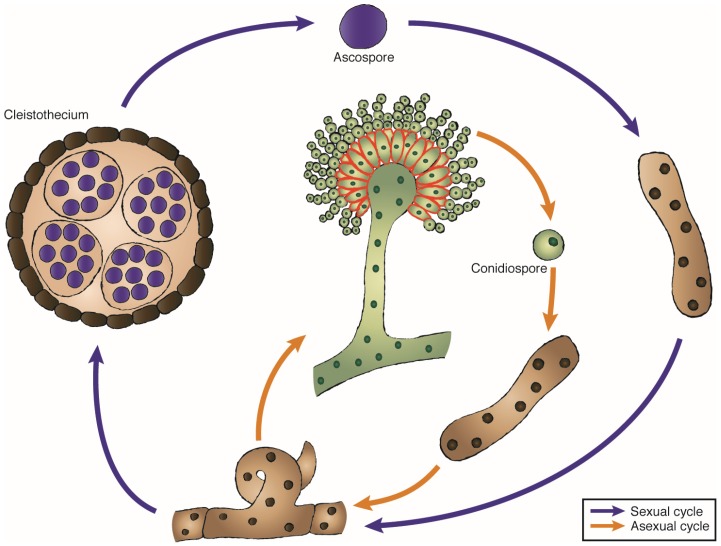
Figure 3.
Life cycle of Aspergillus and suggested localization of ribotoxins. Aspergillus can enter a sexual or an asexual reproductive cycle. During the sexual cycle, the mycelium forms a fruiting body, the cleistothecium, which holds the ascospores that once released into the environment can form a new mycelium. In the asexual reproduction, the mycelium differentiates into identical asexual spores or conidiospores. Ribotoxins would be produced during maturation of the conidia, and would be located on the edge of the phialides (shown in red). Additionally, a parasexual cycle can take place in Aspergillus (not shown).