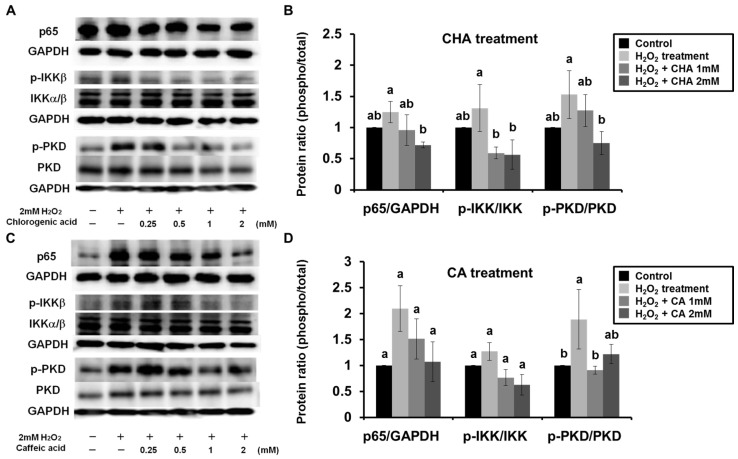
Figure 3.
Chlorogenic acid (CHA) and caffeic acid (CA) suppressed activation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced protein kinase D (PKD)-I-κB kinase (IKK)-nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling. Caco-2 cells were pre-incubated for 3 h with 0.25–2 mM CHA or CA, and then exposed to 2 mM H2O2 for 1 h (p65), 10 min (IKK), or 5 min (PKD). (A) CHA and (C) CA were also added to Caco-2 cells at a concentration equal to that used for pretreatment. For quantification of p65, whole proteins extracted from Caco-2 cells were separated into cytosol and nuclear fractions. In addition, whole proteins extracted from Caco-2 cells were investigated for activation of IKK or PKD by comparing regular and phospho-IKK or phospho-PKD using Western blotting with GAPDH as a housekeeping protein. Data represent three independent experiments, and densitographic analysis of these bands was performed (B,D). Values are mean ± SE (n = 3). Means that have no letter in common are significantly different from each other (p < 0.05) by Tukey’s test.