Fig. 1.
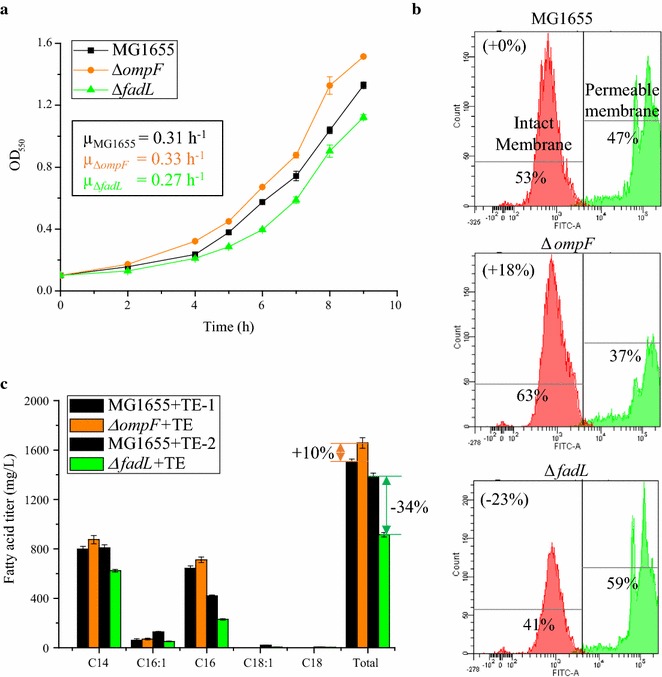
Effects of ompF or fadL deletion on membrane integrity during short-chain fatty acid challenge, short-chain fatty acid tolerance and production of C12 and C14 fatty acids. a Deletion of ompF or fadL impact the specific growth rate relative to the wild type MG1655 during challenge with 10 mM C8. Inset values are the specific growth rate, h−1. b Deletion of ompF or fadL alters the percentage of cells with intact membranes (membrane integrity), assessed using SYTOX Green, during challenge with 10 mM C8. c Deletion of ompF increased fatty acid production and deletion of fadL decreased fatty acid production. MG1655 + TE-1 and MG1655 + TE-2 indicates experiments performed with the same strain, but on different days. For a and b, experiments were performed in MOPS + 2% (wt/v) dextrose shake flasks at 220 rpm 30 °C with an initial pH of 7.0, 10 mM octanoic acid (C8). For c, strains carry the pXZ18Z plasmid (TE) for LCFA (C14–C16) production. Fermentations were performed in MOPS + 2% (wt/v) dextrose shake flasks at 220 rpm 30 °C with an initial pH of 7.0, 1.0 mM IPTG. Values are the average of at least three biological replicates with error bars indicating one standard deviation. Percent increase values are shown only for differences that were deemed statistically significant (P < 0.05)
