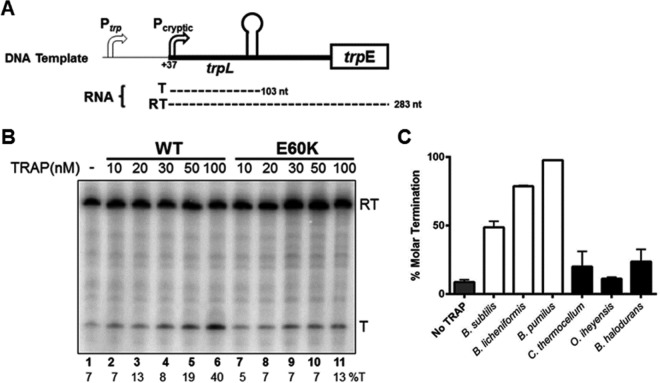
FIG 5.
In vitro attenuation assays. (A) Schematic diagram of the DNA template used for in vitro transcription attenuation assays. Transcription initiates at position +37 (relative to the WT trp promoter), from a cryptic promoter modified to match the consensus −10 and −35 sequences. The two major transcripts produced from this template are shown below the diagram and include a 103-nt transcript that terminates at the trp attenuator (T) and a 283-nt transcript that reads through the attenuator and continues to the end of the template (RT). (B) Representative 6% polyacrylamide–8 M urea gel electrophoresis analysis of the products of in vitro transcription of the trp leader region by use of B. subtilis RNAP. Reactions were performed in the absence or presence of various concentrations of WT or E60K TRAP. Positions of readthrough (RT; 283 nt) and terminated (T; 103 nt) transcripts are indicated on the right. The percentage of transcripts terminating at the attenuator (%T) for each reaction is shown at the bottom of each lane. (C) Bar graph representation of average percent termination from three independent analyses of in vitro transcription attenuation in the absence or presence of 100 nM TRAPs from several bacterial species. The TRAPs examined contained either an acidic (open bars) or basic (closed bars) residue at position 60.