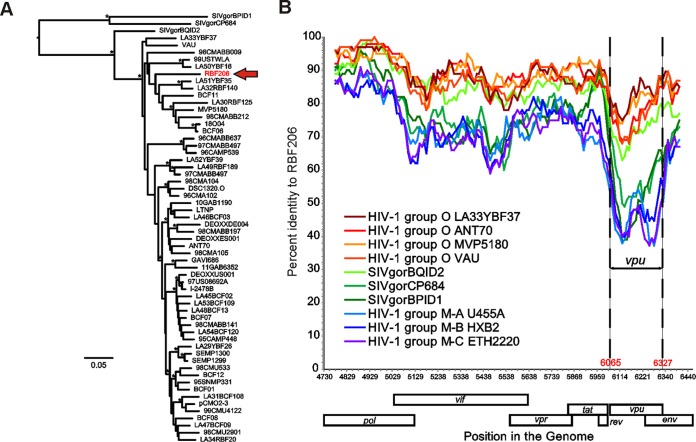
FIG 2.
Evolutionary relationship of RBF206 to other HIV-1 group O strains. (A) A maximum likelihood tree illustrating the phylogenetic relationship of RBF206 (highlighted in red) to other HIV-1 group O strains is shown for the central region spanning from the 3′ end of pol to the 5′ end of env (HXB2 coordinates 4730 to 6459; 1,638 bp). The tree is rooted using SIVgor sequences as outgroups. Asterisks indicate bootstrap values of ≥95% (the scale bar represents 5 substitutions per 100 sites). (B) The percent sequence identity of RBF206 to selected HIV-1 group O (orange and red), group M (blue), and SIVgor (green) sequences is plotted for a 1,619-bp region located between the 3′ end of pol and the 5′ end of env (HXB2 coordinates 4730 to 6459). Pairwise sequence distances were calculated for a 100-bp window, moved in increments of 10 bp along the alignment. The vpu coding region is shown (coordinates 6065 to 6327). The x axis indicates the genome position along the alignment (HXB2 coordinates), while the y axis shows sequence identity. Regions that could not be unambiguously aligned and sites with gaps were removed from the analysis. GenBank or DDBJ accession numbers for the sequences are for HIV-1 group O are as follows: LA33YBF37, KU168285; ANT70, L20587; MVP5180, L20571; and VAU, AF407418. Accession numbers for SIVgor are as follows: BQID2, KP004991; CP684, FJ424871; and BPID1, KP004989. Accession numbers for HIV-1 group M are as follows: subtype A U455A, M62320; subtype B HXB2, K03455; and subtype C ETH2220, U46016.