FIG 1.
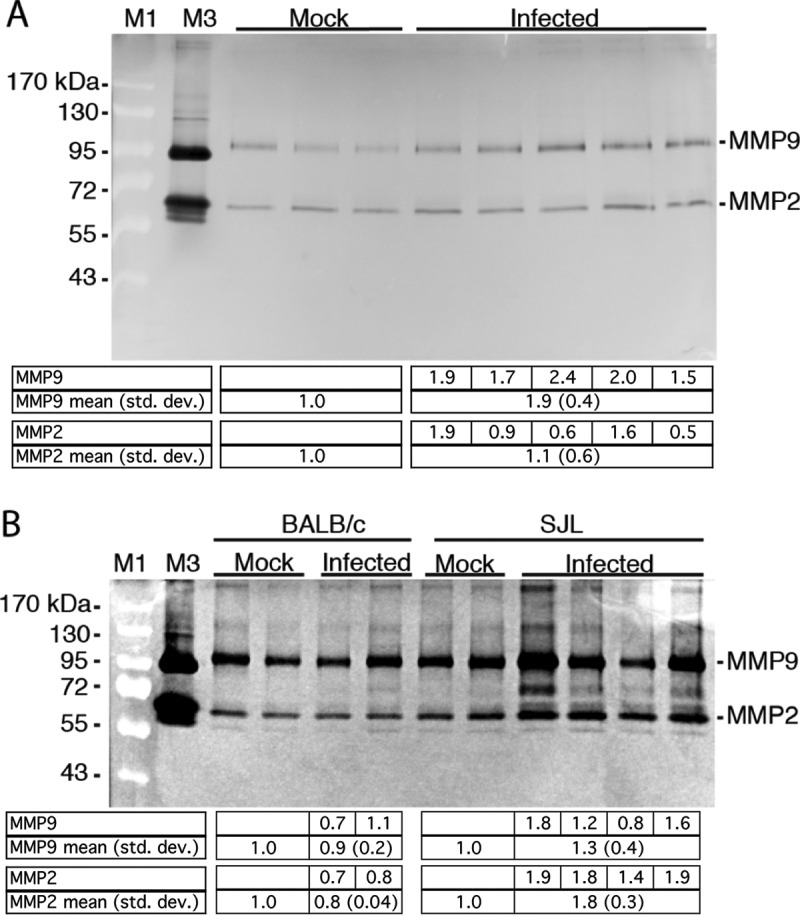
MAV-1 infection increases MMP activity in brains. (A) Five-week-old SJL mice were mock infected (n = 3) or infected i.p. with 105 PFU of MAV-1 (n = 5) and euthanized 3 dpi. Brain homogenates (200 mg) were analyzed by gelatin zymography. The higher level of MMP9 in infected brains was statistically significant (P = 0.04; Mann-Whitney test). (B) Six-week old BALB/c or SJL mice were mock infected (n = 2) or infected i.p. with 102 PFU MAV-1 (BALB/c, n = 2; SJL, n = 4) and euthanized 8 dpi. Brain homogenates (600 mg) were analyzed by zymography. The differences between mock-infected and infected or between infected BALB/c and SJL mice were not statistically significant (Mann-Whitney test). M1, molecular mass standards (indicated on the left); M3, human HT1080 cell supernatant (proMMP9, 92 kDa; MMP2, 72 and 62 kDa). The levels of MMP activity were quantitated by densitometry and normalized to the mean for the mock-infected samples. Individual values are listed for the infected mice, and the means and standard deviations (std. dev.) are listed for the corresponding lanes below the gels.
