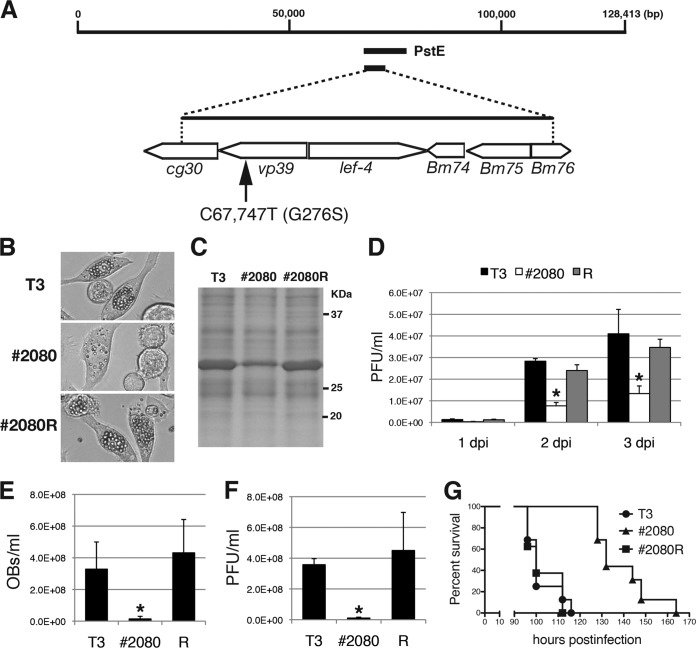
FIG 2.
Marker rescue experiments for #2080. (A) Marker rescue of #2080. BmN-4 cells were transfected with #2080 genomic DNA and BmNPV genomic libraries. One genomic library, PstE, rescued the FP phenotype of #2080. Transfection with subcloned genomic fragments revealed that the responsible mutation(s) existed within the 5-kbp-long fragment. DNA sequencing identified a single nucleotide mutation at nt 67,747 (C to T), resulting in an amino acid substitution at Gly-276 of the major capsid protein VP39. (B) Light microscopic observations at 3 dpi of BmN-4 cells infected with T3, #2080, or a repair virus (#2080R). (C) POLH expression. At 3 dpi, the cell lysate of BmNPV-infected cells was subjected to SDS-PAGE, and a gel stained with Coomassie brilliant blue is shown. (D) Cellular BV production. The BV titers in BmN-4 cells at 1, 2, or 3 dpi were determined by plaque assay. Data are presented as the mean ± SD from triplicate experiments. R, #2080R. *, P < 0.05, one-way analysis of variance with Tukey's posttest in comparison to T3. (E) Larval OB release. The numbers of OBs released in the hemolymph of BmNPV-infected B. mori larvae were quantified at 4 dpi (n = 4). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. *, P < 0.05, one-way analysis of variance with Tukey's posttest in comparison to T3. (F) Larval BV production. The BV titer in the hemolymph of BmNPV-infected B. mori larvae at 4 dpi was determined by plaque assay (n = 4). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. *, P < 0.05, one-way analysis of variance with Tukey's posttest in comparison to T3. (G) Survival curves for B. mori larvae infected with T3, #2080, or #2080R. The LT50s of T3, #2080, and #2080R were 100, 132, and 100 h, respectively (n = 16).