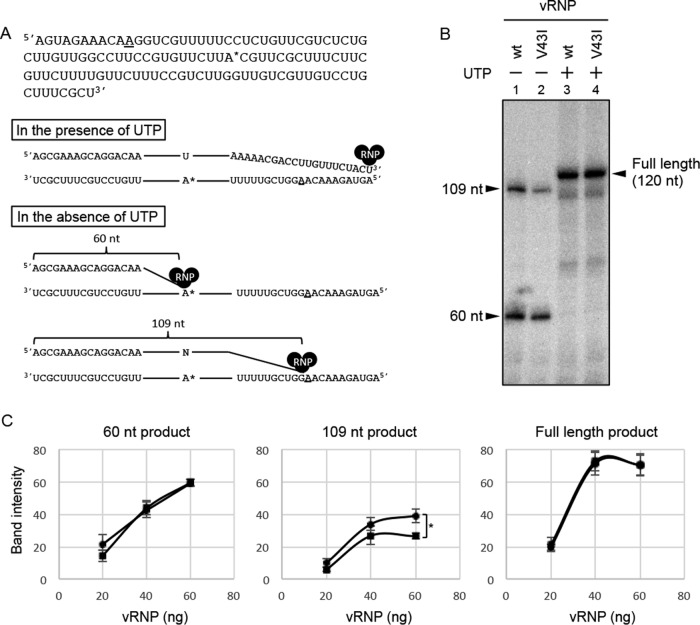
FIG 2.
PB1-Val-43 residue is determinant of fidelity. (A) Illustration of an in vitro limited elongation assay using a 120-nt model viral RNA template. In the presence of UTP, viral polymerase generates the full-length RNA product (120 nt). In the absence of UTP, RNA synthesis was paused at the first adenine residue at nucleotide position 61 from the 3′ terminus. The synthesized RNA was elongated at a second adenine residue (nucleotide position 110 from the 3′ terminus) by misincorporation of nucleotides at the first adenine residue. The first and the second adenines from the 3′ terminus are indicated by an asterisk and underlining, respectively. (B) Reaction products from vRNP-catalyzed nucleotide incorporation under the indicated condition. A limited elongation assay was carried out with the 120-nt model vRNA and 40 ng of vRNP at 37°C for 1 h in the absence (lanes 1 and 2) or presence (lanes 3 and 4) of UTP. (C) PB1-V43I polymerase is more faithful than the wild-type enzyme. A limited elongation assay was carried out under the same conditions as for the experiment shown in panel B using 20 ng, 40 ng, and 60 ng of vRNP. The amounts of the RNA products of 60 nt, 109 nt, and 120 nt derived from the PB1-V43I mutant were compared with those of the PB1 wild type. Band intensities (shown as arbitrary units) were determined after subtraction of the background using ImageJ, version 1.4.3.67, image analysis software. Quantitative results are presented as the averages with the standard deviations from at least three independent experiments. Significance was determined using Student's t test (*, P < 0.05). Circles, vRNP of PB1 wild type; squares, vRNP of PB1-V43I. wt, wild type.