Fig. 1.
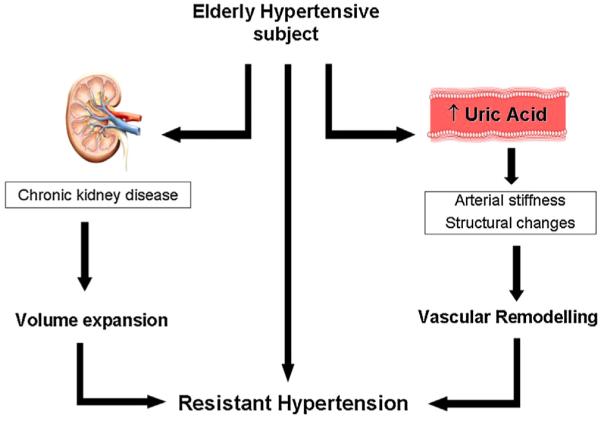
The proposed mechanisms supporting resistant hypertension development in the hypertensive elderly subjects are shown. Chronic kidney disease and hyperuricemia (i.e. serum uric acid ≥6.8 mg/dl) independently increase the risk of resistant hypertension by volume expansion (left side) and vascular remodelling respectively (right side).
