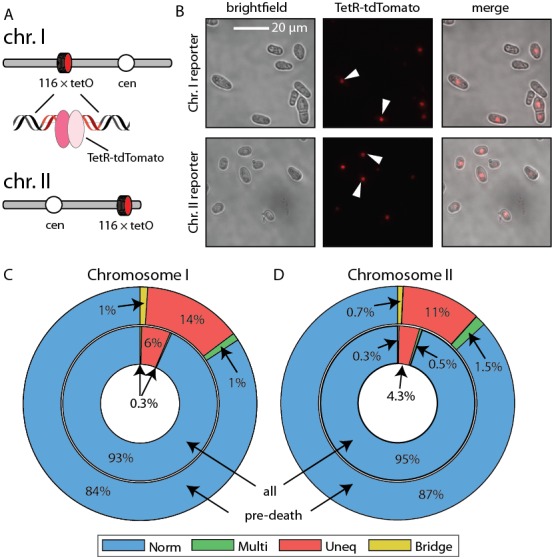
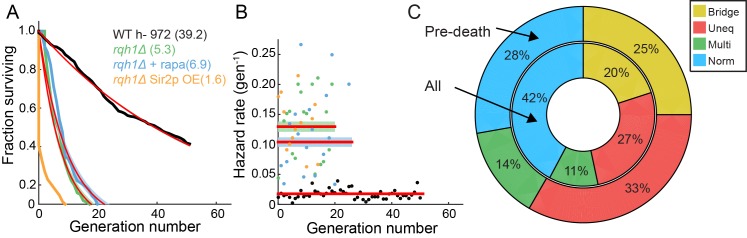
Figure 6. Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) instability is highly correlated with cell death.
(A) Images of cells exhibiting rDNA instability, as reported by gar2-mCherry, which binds to rDNA. (B) Likelihood of cell death following one of the defects observed in (A). (C) Dying cells exhibited elevated rDNA defects (outer ring) relative to healthy dividing cells (inner ring).
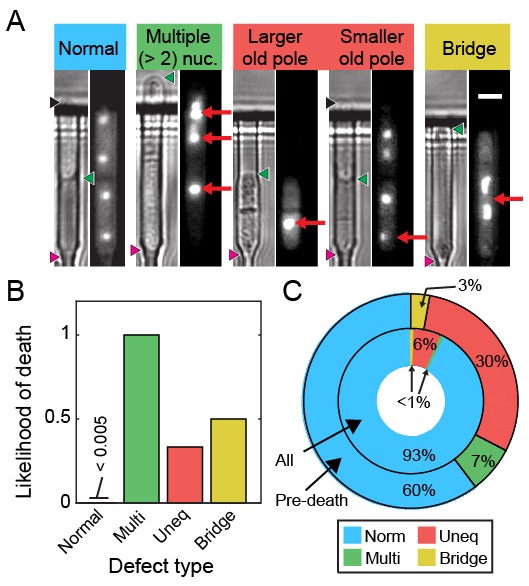
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Strains expressing gar2-mCherry maintain wild-type replication rates.
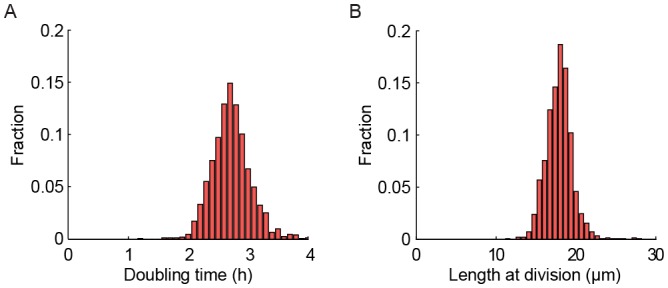
Figure 6—figure supplement 2. Live imaging of chromosome mis-segregation rates.