Figure 1.
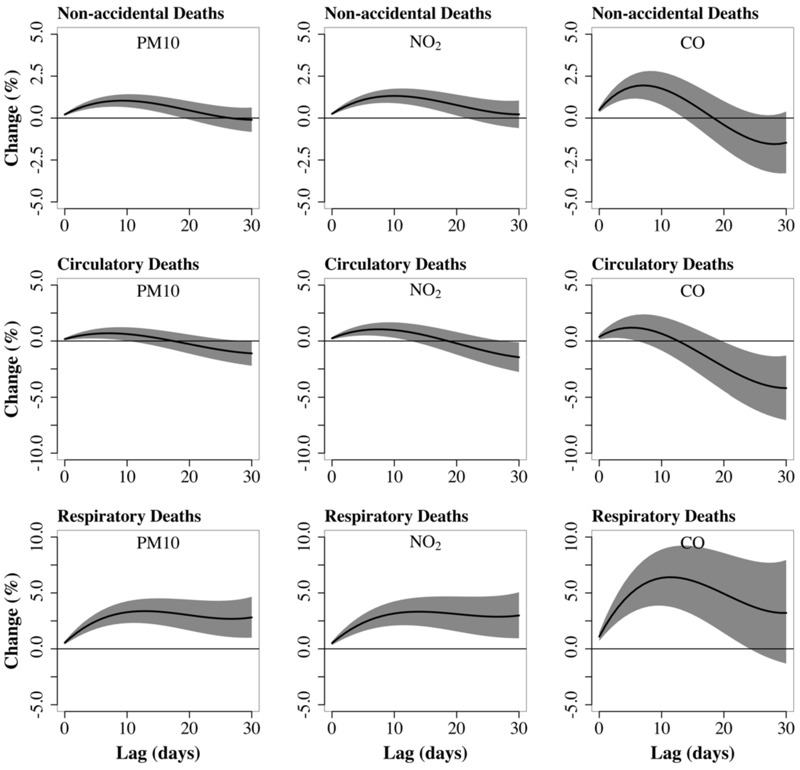
Cumulative percent changea in number of deaths associated with air pollutant levels of lag 0–30 days.b aAssociated with a 10-μg/m3 increase in particulate matter smaller than 10 μm (PM10) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and with a 1-ppm increase in carbon monoxide (CO). bResults from a Poisson generalized additive distributed lag model, constrained with a second degree polynomial, using cumulative lag structures of lags 0–30 days for PM10, NO2, and CO, adjusted by trend, seasonality, temperature, relative humidity, weekdays, and holidays. The shadow area represents the 95% confidence interval.
