Figure 2.
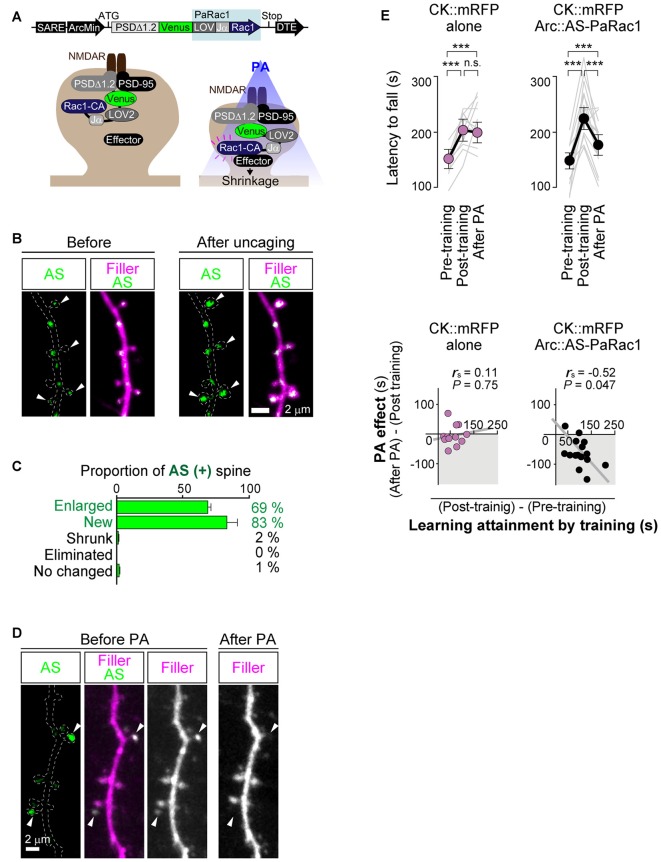
Selective labeling and shrinkage of potentiated synapses by AS-PaRac1. (A) Schematic representation of the AS-PaRac1 vector, which was transcribed under the control of synaptic activity-responsive element (SARE) and the Arc minimal promoter. The LOV2 domain was attached to the N terminus of the constitutively active form of Rac1 (Rac1-CA), blocking the effector binding site of Rac1 until the blue light irradiation led to the unwinding of the LOV Jα helix. Therefore, Rac1 activity could be controlled by blue light, enabling optical control of spine shrinkage. (B) Protein synthesis-dependent potentiation during the single spine LTP protocol, which was elicited by glutamate uncaging in the presence of the adenylyl cyclase activator forskolin, induced the accumulation of AS-PaRac1 in the stimulated spines (arrowheads). Hippocampal slice culture (DIV 11). (C) AS-PaRac1 labeling in vivo during the rotarod task. Percentage of AS-PaRac1-containing spines for enlarged (Δ spine volume ≥ 50%), newly formed, shrunk (Δ spine volume ≥ −50%) and eliminated spines following the rotarod task. (D) Selective shrinkage of AS-PaRac1-positive spines by photoactivation (PA). Neurons in the hippocampal slice culture (DIV 11) were biolistically transfected with AS-PaRac1-Venus and filler. Robust shrinkage (arrowheads) was observed, while AS-PaRac1-negative spines were not affected by PA, despite being located adjacent to the AS-PaRac1-positive spines. (E) Erasure of the acquired learning by PA of the potentiated spines labeled with AS-PaRac1. The mice were divided into two groups: animals in the first group were infected with CaMKII promoter::mRFP (CK::mRFP) alone as a control, while those in the second group were infected with AS-PaRac1 and mRFP in the primary motor cortex (M1). Both the groups exhibited significantly better motor performance after training (Post-training), but only the performance of the AS-PaRac1 group was disturbed by PA (After PA), and the extent of learning disruption induced by PA (PA effect) negatively correlated with the extent of training-evoked improvement (learning attainment). In contrast, there was neither a disruption of acquired learning nor a correlation between the effects of training and of PA in the control group. One-way repeated measures ANOVA for the comparison of task performance for the same subjects at different time points followed by post hoc Scheffé’s test (***P < 0.001) and Spearman’s rank correlation were used. Abbreviations: AS-PaRac1, Activated Synapse-targeting PhotoActivatable Rac1; DIV, days in vitro; LTP, long-term potentiation; CaMKII, Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; mRFP, monomer red fluorescent protein; ANOVA, analysis of variance. Image adapted, with permission, from Hayashi-Takagi et al. (2015).