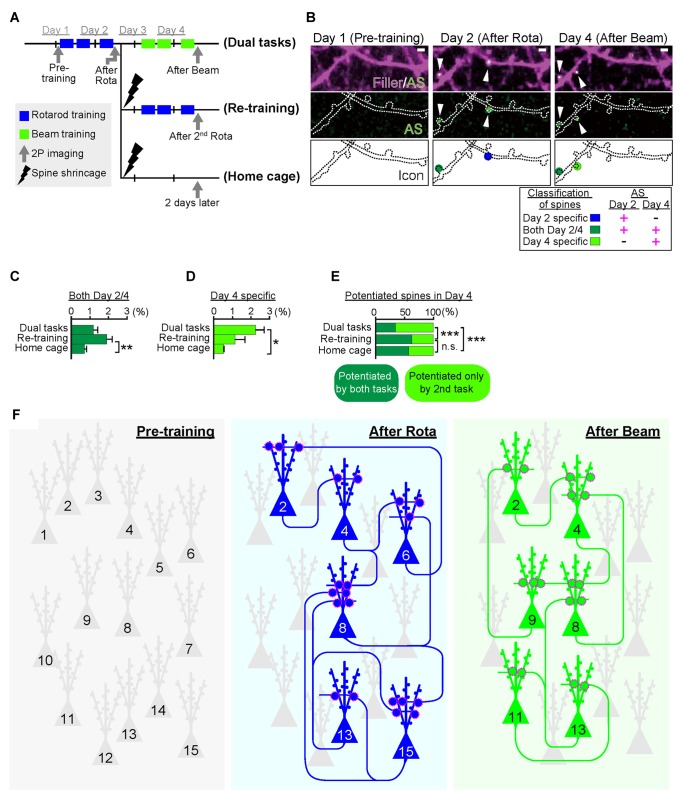
Figure 3.
Task-specific synaptic ensembles. (A) Experimental design. Layer II/III pyramidal neurons in the M1 were sparsely transduced with Arc::AS-PaRac1-Venus and CAG::mRFP (filler). Mice were subjected to distinct training protocols. In the dual task protocol, mice sequentially learned two distinct hindlimb tasks: the rotarod and beam tasks in the first and the latter 2 days, respectively. The re-training protocol group was subjected to the rotarod task in the first 2 days, which was followed by the shrinkage of the learning-evoked potentiation by PA, and then the identical rotarod task was re-trained. The homecage group was subjected to the rotarod task and subsequent PA, and mice were not touched or trained for another 2 days. (B) Representative images of dendrites that exhibited potentiation during learning. AS-PaRac1 puncta are color-coded based on the appearance and duration of fluorescence: the rotarod task potentiation (day 2-specific, blue), beam task-specific potentiation (day 4-specific, greenish yellow), and continuous potentiation for both periods (both day 2 and 4, dark green). (C) Significant increase was seen in the potentiation on both days 2 and 4 in the re-training group, suggesting that re-training induced re-potentiation of the same subset of spines. (D,E) The proportion of newly potentiated spines, which had not been potentiated in the first 2 days, significantly increased only in the dual task group. (F) Conceptual comparison between cell ensembles and synaptic ensembles. The schema was depicted based on our findings that the cell ensembles for the rotarod and beam tasks was significantly more overlapping than the synaptic ensembles. The difference in pattern between cell ensembles and synaptic ensembles supports the importance of visualization of synaptic ensembles as well as that of cell ensembles to understand how the brain is reorganized during learning and memory. Statistical significance was tested with ANOVA followed by post hoc Scheffé’s test for (C, D), and Chi-square test was used to test independence for (E). For all statistical test *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 were considered significant. n.s., not significant. Abbreviations: AS-PaRac1, Activated Synapse-targeting PhotoActivatable Rac1; mRFP, monomeric red fluorescent protein; ANOVA, analysis of variance. Images from (A–E), adapted, with permission, from Hayashi-Takagi et al. (2015).