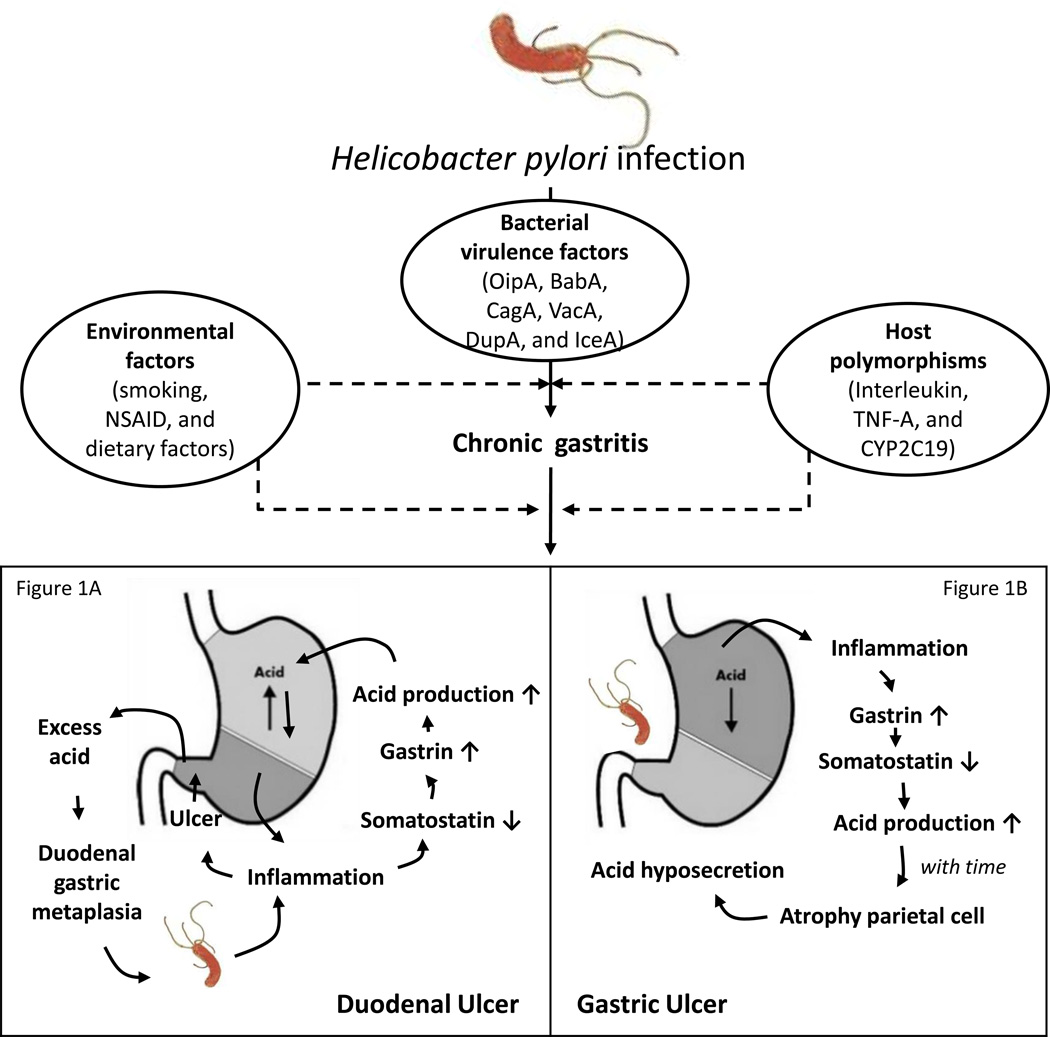
Figure 1. The opposite ends of the peptic ulcer disease (PUD) spectrum.
Genetic polymorphisms in conjunction with bacterial and/or environmental factors including a combination of markers from the adaptive and innate immune systems are involved in the response to H. pylori infection. Duodenal ulcer (DU) is usually related to high antral inflammatory scores, and high acid secretion (Figure 1A). Gastric ulcer (GU) is related to corporal gastritis or pangastritis and normal or decreased acid secretion (Figure 1B).