Figure 5.
Cells Deficient for the Short ASCC3 Isoform Cannot Recover Transcription after UV Irradiation
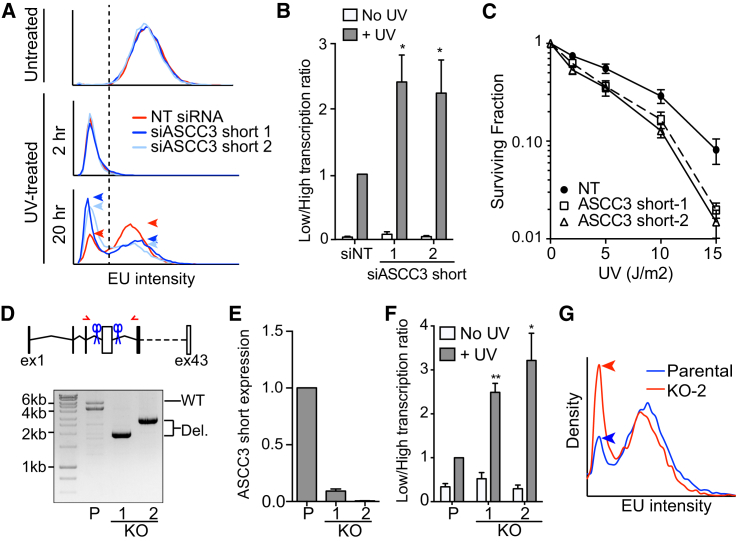
(A) As in Figure 4E, but after knockdown of the short ASCC3 isoform with individual siRNAs (light and dark blue).
(B) As in Figure 4F, but after knockdown of short isoform. Data are mean ±SEM relative to UV-treated control.
(C) UV-sensitivity measured by colony formation after knockdown with individual siRNAs targeting ASCC3 short isoform. Two-way ANOVA test: NT versus ASCC3 siRNA-1 p = 0.0182; NT versus ASCC3 siRNA-2 p = 0.008.
(D) CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knockout of the unique, terminal exon of the short ASCC3 isoform. Genomic PCR fragments isolated from parental MRC5VA cells (P) and two knockout (KO) clones are shown (red arrows, primers; blue scissors, guide RNAs).
(E) qRT-PCR analysis of short isoform RNA expression in the cell lines from (D), showing averaged GAPDH-normalized data, relative to parental cells.
(F) Transcription recovery after deletion of the short ASCC3 isoform, measured as in Figures 4F and 5B.
(G) Histograms showing decreased EU intensity/nucleus in ASCC3 short isoform KO clone-2 cells compared to control cells 20 hr after UV irradiation.
See also Figure S5.