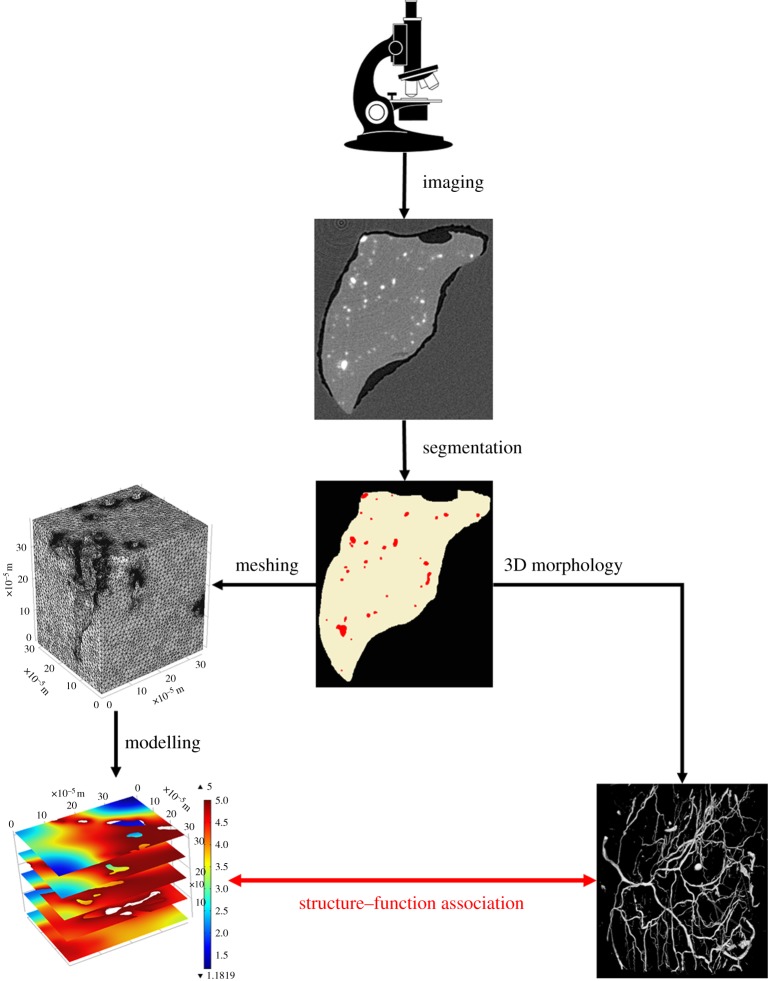
Figure 2.
Generic workflow for image-based modelling. Images are acquired by a specific imaging technique. From the resulting images, blood vessels and muscle tissue can be segmented from the background material (here wax). The blood vessels can now be analysed for their 3D structure by quantitative morphometry. At the same time, the segmented tissues can be meshed for finite-element modelling. The mesh is then imported into a partial differential equation solver, which will solve equations describing the biological process at hand. Given the results of the quantitative morphometry and the solved mathematical model, an association between 3D vascular structure and function can be derived, for instance in terms of fluid flow or tissue oxygenation. Microscope clipart from © 2014 ClipartPanda.com. (Online version in colour.)