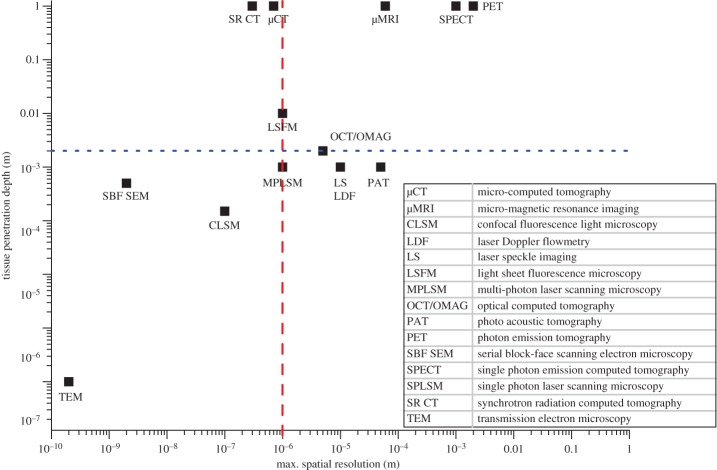
Figure 4.
Comparison of different imaging techniques with regard to maximum spatial resolution and tissue penetration depth. The dashed red line marks 1 µm, which is the spatial resolution required to resolve capillaries. The dotted blue line indicates the minimal tissue penetration depth required to image a whole organ non-invasively, based on murine muscle dimensions of about 0.2 × 0.2 × 0.8 cm3. The top left quadrant covers high-resolution 3D imaging techniques that are appropriate to assess the (muscle) microvasculature and includes micro-computed tomography (µCT), synchrotron-based CT (SR CT) and at the limit light sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM). (Online version in colour.)