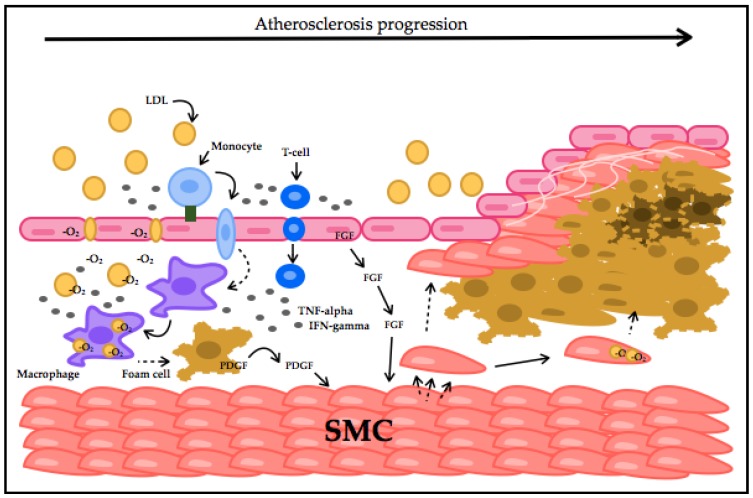
Figure 1.
Atherosclerotic plaque formation process. LDLs at a high concentration inhibit endothelial cells’ (EC) endocytosis capacity, migrate and accumulate in the intima. LDLs get oxidized and induce VCAM (green square) expression in EC. Monocytes are recruited into the intima by VCAM interaction. Monocytes transform into macrophages, which take-up oxLDLs, forming foam cells. Macrophages and EC secrete chemokines and recruit T-cells. T-cells produce TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma, amplifying inflammation. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulate smooth-muscle cells (SMC) migration and proliferation. SMCs can also accumulate lipids, migrate and proliferate. A lipid core is generated with necrotic foam cells surrounded by SMCs and a collagen fibrous cap, resulting in thrombus formation.