Figure 5.
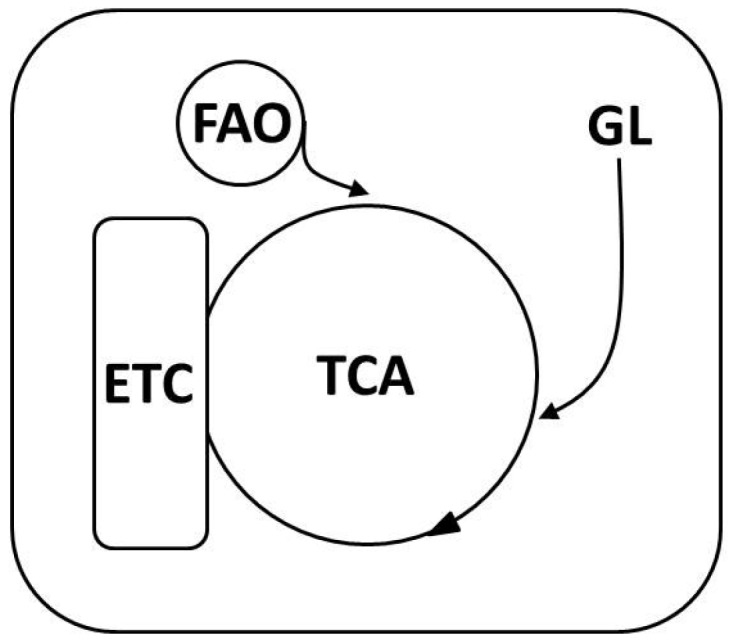
Molecular pathways associated with CVD etiology. Contributing CVD factors, such as diabetes, cause an imbalance of essential physiological pathways by impairing normal glycolysis (GL), which feeds into the tricarboxylic acid pathway (TCA) that is directly linked to the electron transport chain (ETC). Fatty acids, which can also contribute and feed into the TCA cycle through fatty acid oxidation (FAO), are also implicated in CVD manifestation. Multiple enzymes involved in this scheme have been shown to either modulate or directly generate ROS.
