Figure 8.
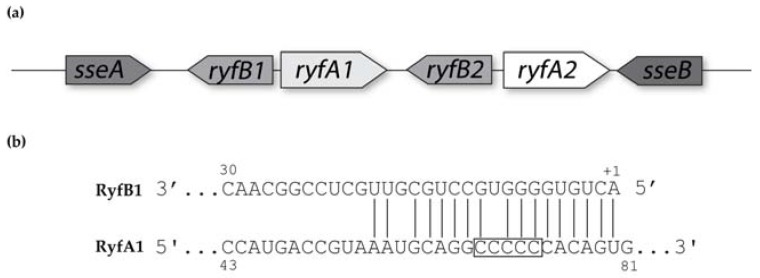
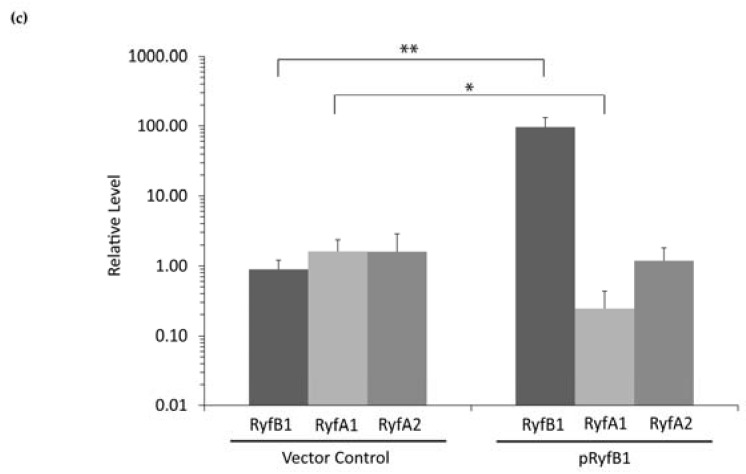
RyfB1 specifically inhibits RyfA1. (a) Next-generation sequencing revealed ≈100 nt long transcripts immediately preceding, and divergent to, ryfA1 and ryfA2. The gene preceding ryfA1 has been termed ryfB1, while that preceding ryfA2 has been termed ryfB2. (b) In silico analyses of RyfB1 revealed a region, in which 16 of 18 nucleotides share complementarity to sequences within RyfA1. Of note, this region of complementarity between RyfA1 and RyfB1 overlaps the five-nucleotide variable region of the latter, indicated by the black box. Numbers indicate the base location relative to the 5′ end of each molecule (+1). (c) qRT-PCR analyses of the relative levels of RyfB1, RyfA1, and RyfA2 in S. dysenteriae carrying the RyfB1-producing plasmid pRyfB1 or the vector control following growth of both strains under inducing conditions. The relative abundance of each target was calculated using the ΔΔCt method [25], in which target transcript levels are normalized to the level of rrsA present in each sample and are expressed relative to the level in that target in a single vector control sample. Data are the average of biological triplicates and errors bars indicate one standard deviation. * denotes a significant difference with p < 0.01 while ** denotes a significant difference with p < 0.001.