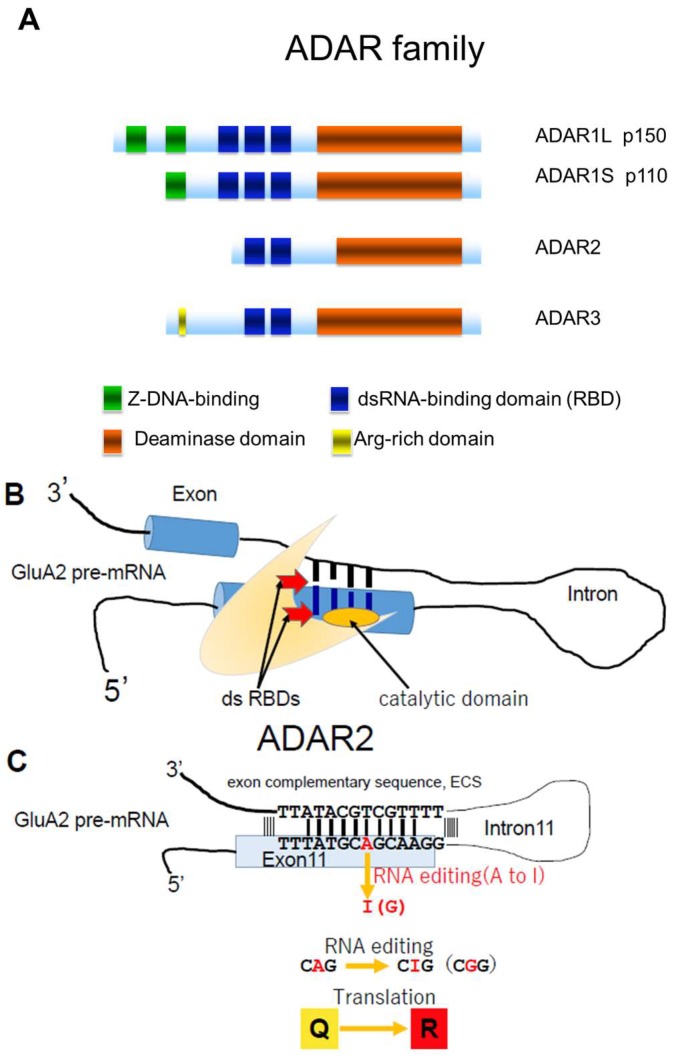
Figure 2.
Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA (ADAR) structure and RNA editing. (A) Three members of the ADAR family. ADAR1 has two isoforms (p150 and p110). ADAR1p110 exists in the nucleus and ADAR1p150 exists in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. ADAR2 is primarily localized in the nucleus of brain and spinal cord and catalyzes A-to-I conversion at the GluA2 glutamine/arginine (Q/R) site. Z-DNA-binding domain (green), RBD; double strand RNA (dsRNA) binding domain (blue), deaminase domain (orange), and arginine-rich domain (yellow); (B) ADAR2 has a double-stranded (ds) RNA binding domain (RBD; red) and a deaminase domain (orange); (C) dsRNA is formed at the distal end of exon 11, which includes the coding sequence for the Q/R site and the exon complementary sequence (ECS) in intron 11 of GluA2 pre-mRNA. ADAR2 catalyzes conversion of adenosine to inosine (A-to-I RNA editing) in the dsRNA structure in both coding and non-coding regions of various transcripts. The adenosine at the Q/R site of GluA2 pre-mRNA is converted to inosine (A-to-I conversion), the genomic CAG (codon for Q) is converted to CIG in mRNA, and CIG is read as CGG, which is a codon for R during translation.