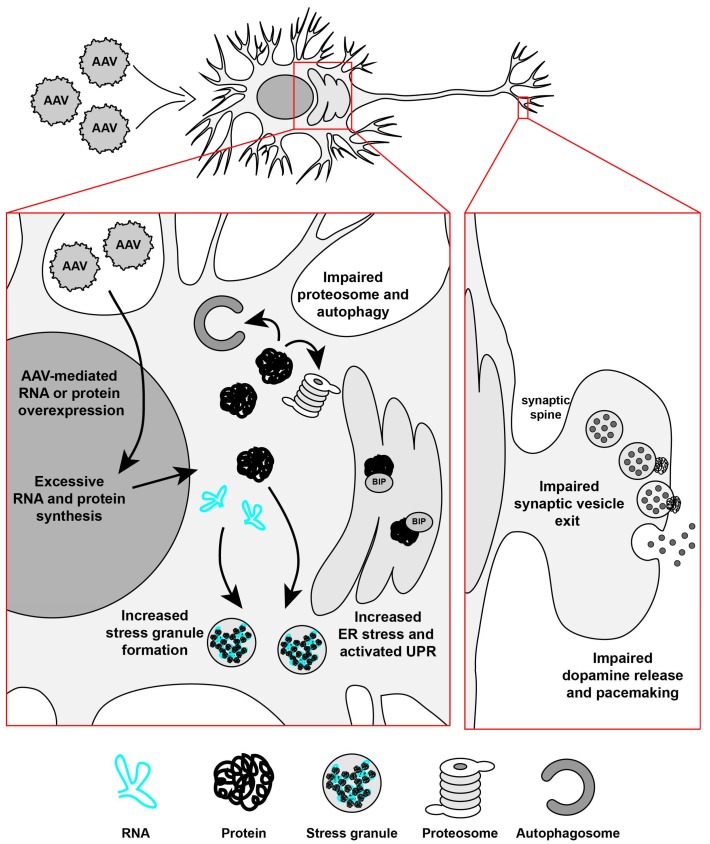
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of protein overexpression via AAV in the substantia nigra dopamine neurons. When an AAV carrying protein or RNA is expressed in the brain, particularly in the substantia nigra where dopamine neurons are vulnerable to stress, the consequences of excessive overexpression may result in a number of events detrimental to cell survival. These include the increased formation of stress granules, increased levels of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR), and impairment of the proteasome function and autophagy. This could further result in impairments in vesicle fusion at the synapse and difficulties in the dopamine release and pacemaking functions of the neuron. This would culminate in reduced neuronal activity and may result in the death of the neuron. (BIP: Binding immunoglobulin protein).