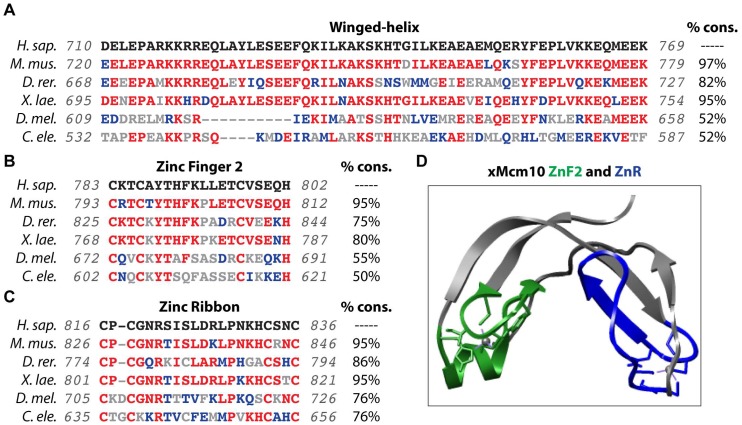
Figure 4.
Evolutionary conservation of functional domains in the Mcm10 CTD. (A–C) Comparison of the amino acid sequences from H. sapiens, M. musculus, D. rerio, X. laevis, D. melanogaster and C. elegans of the Winged Helix (A), Zinc-Finger 2 (B) and Zinc-Ribbon (C). The percent conservation (% cons.), defined as the percentage of amino acid positions identical (in red) or strongly similar (in blue) to those of human Mcm10, is listed for each domain sequence. The total region aligned for each sequence listed in gray. (D) The crystal structure of the Xenopus Mcm10 (xMcm10) Zinc-Finger 2 (green) and Zinc-Ribbon (blue) domains is shown. The structure was generated using pdb data file 2KWQ and the Chimera program (http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera) [83].