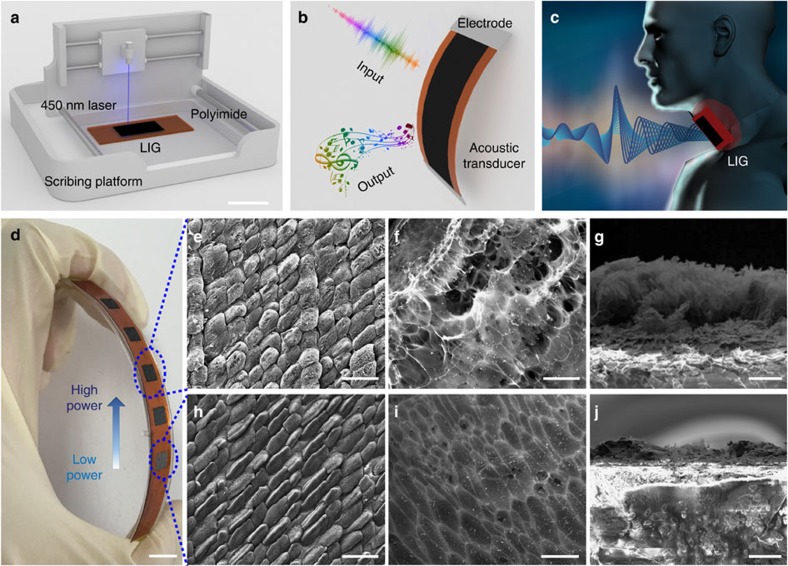
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the fabrication process and the morphology of LIG.
(a) One-step fabrication process of LIG. PI is directly converted into LIG by the irradiation of the 450 nm laser. Scale bar, 2.5 cm. (b) LIG has the ability of emitting and detecting sound in one device. (c) The artificial throat can detect the movement of throat and generate controllable sound, respectively. (d) Six LIG samples produced by 450 nm laser with different power ranging from 20 to 350 mW. Scale bar, 5 mm. (e) The morphology of LIG sample produced at 290 mW under scanning electron microscopy. Scale bar, 150 μm. (f) The morphology of LIG sample produced at 290 mW under high magnification. Scale bar, 5 μm. (g) Cross-sectional view of LIG sample produced at 290 mW. Scale bar, 12.5 μm. (h) The morphology of LIG sample produced at 125 mW under scanning electron microscopy. Scale bar, 150 μm. (i) The morphology of LIG sample produced at 125 mW under high magnification. Scale bar, 5 μm. (j) Cross-sectional view of LIG sample produced at 125 mW. Scale bar, 12.5 μm.