Figure 1.
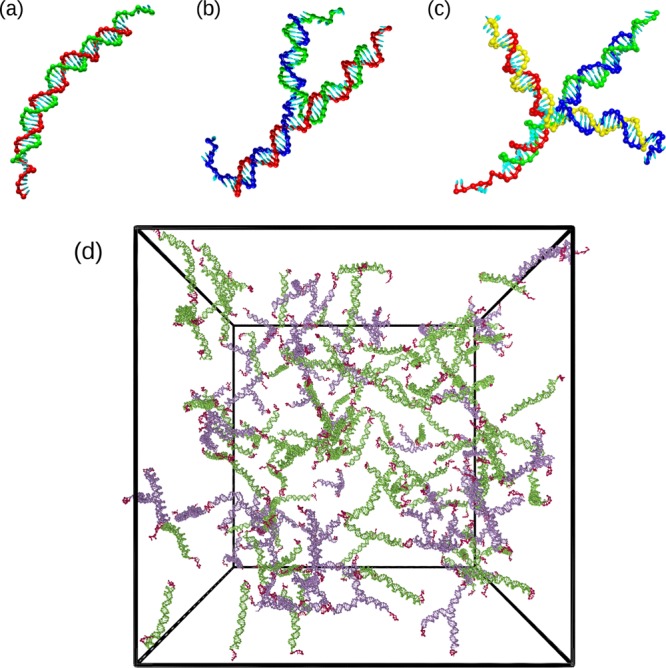
(a–c) Representative snapshots of DNA nanostars with different functionalities. (a) A DNA dimer (f = 2), (b) a DNA trimer (f = 3), and (c) a DNA tetramer (f = 4). The f strands composing each nanostar are colored differently. (d) Simulation snapshot of a binary mixture composed of 50 trimers and 100 dimers at a nanostar number density ρ = 2.4 × 10–4 nm–3 and T = 48 °C. Trimers are colored violet, dimers are green, and sticky ends are red.
