Figure 13.
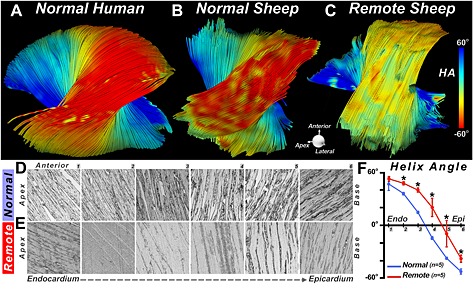
DTI‐tractography ex vivo showing a rightward rotation of fibers in the remote zone of a myocardial infarct. (A, B) Fiber tracts in the lateral wall of (A) a normal human heart and (B) a normal sheep heart. (C) Fiber tracts in the lateral wall (remote zone) of a sheep with a large septal infarct. The fibers in the remote zone have undergone a rightward (more positive) shift in HA. This can be clearly seen in the epicardium, where the fibers have shifted from red to yellow. (D–F) Histological confirmation of the DTI‐tractography findings. (D, E) Sections were obtained at six transmural depths in the lateral wall (1–6, from endocardium to epicardium) of normal sheep (D) and the remote zone (E) of infarcted sheep. (F) The transmural slope of HA, calculated from the histological sections, shows that HA in the remote zone becomes more positive (normal versus remote: * p < 0.05). Reproduced with permission 21.
