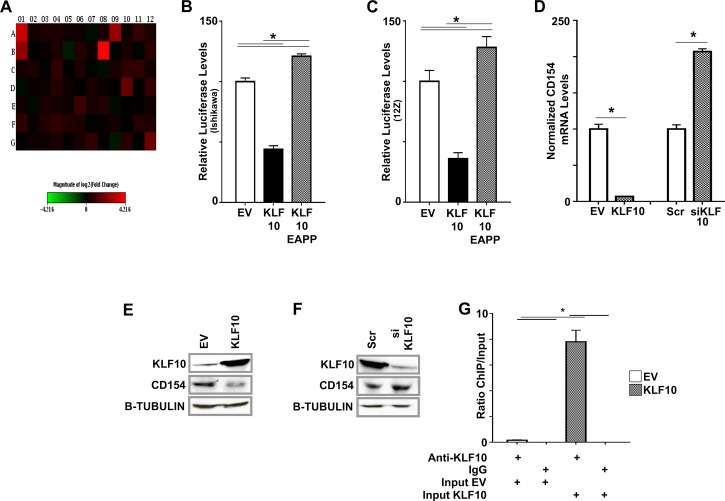
FIG. 5.
KLF10 binds to and regulates CD154. A) Heat map showing expression of 84 innate and acquired immune-related genes determined using PCR arrays in Ishikawa cells transfected with Scr and KLF10 siKLF10. The results were normalized to the expression of five housekeeping genes and represent the average fold change from three independent biological replicates. Decrease in KLF10 resulted in a statistically significant elevation in expression of CD40 (A12) and CD154 (B1) at 1.36 and 5.3 fold, respectively (P < 0.05 based on three biological replicates). Complete list of altered genes is provided in Supplemental Table S1. B, C) Ishikawa cells (B) and 12Z cells (C) were cotransfected with pcDNA3/HIS (EV), pcDNA3/HIS-KLF10, or pcDNA3/HIS-KLF10EAPP and a pGL4/CD154-promoter-reporter construct. KLF10 repressed CD154-promoter luciferase activity compared to EV (*P < 0.05 compared to EV). In contrast, KLF10EAPP derepressed and thus activated CD154 promoter luciferase expression (*P < 0.05, compared to KLF10 and EV as indicated). Luciferase levels were normalized to total lysate protein concentration. Assays were repeated in triplicate three times. D) Overexpression of KLF10 in Ishikawa cells decreased normalized CD154 mRNA expression 9 fold compared to EV. In contrast, CD154 mRNA expression levels were significantly increased in Ishikawa cells transfected with KLF10 siRNA compared to Scr control. CD154 mRNA expression was normalized to five housekeeping genes (mean expression levels ± SEM shown, *P < 0.05). E) KLF10 overexpression in Ishikawa cells transfected with pcDNA3/HIS-KLF10 cognately suppressed CD154 protein expression compared to corresponding EV. Beta-TUBULIN was used as a loading control. F) Conversely, suppressed transcription factor expression in cells transfected with KLF10siRNA was associated with increased CD154 protein expression compared to that in cells transfected with scrambled control (Scr). Beta-TUBULIN was used as a loading control. G) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay was used to determine direct KLF10 binding to the region −600 to −401 of the CD154 promoter in Ishikawa cells. Promoter binding was detected by anti-KLF10 but not a control species- and isotype-specific IgG. Promoter-transcription factor binding was increased nearly 8 fold in cells transfected with pcDNA3/His KLF10 compared to EV. Levels were normalized to input (diluted 1:100). *P < 0.05 for comparisons of normalized binding levels in EV or KLF10-transfected cells analyzed by ChIP using anti-KLF10 or IgG as well as for comparison of normalized binding levels in EV and KLF10-transfected cells analyzed by ChIP using anti-KLF10 as indicated.