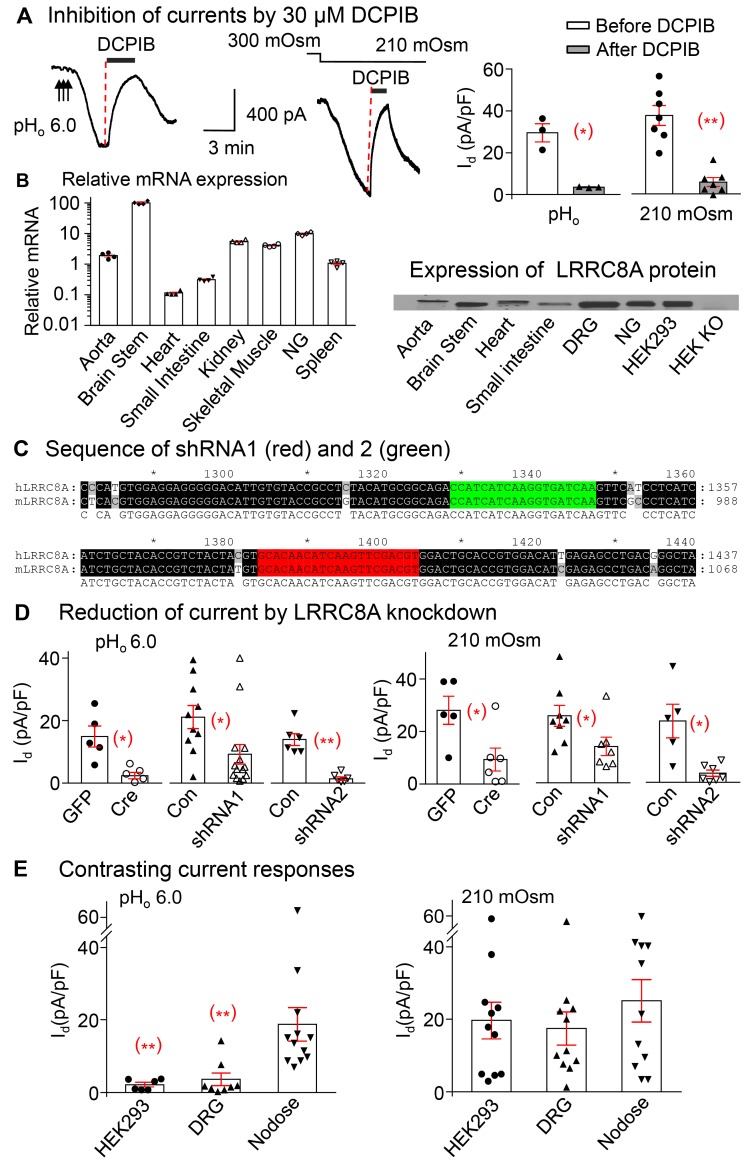
Figure 3. Leucine-rich repeat containing protein 8A (LRRC8A) in nodose neurons is essential for activation of low pHo–conditioned and hypoosmolarity-induced Cl– currents.
(A) The tracings and panels show that the pHo-conditioned current densities (Id) induced by pHo 6.0 is inhibited from 29.5 ± 4.3 pA/pF to 3.5 ± 0.2 pA/pF after application of 30 μM DCPIB, the blocker of VRAC/LRRC8 (n = 2 mice, *P < 0.05). Similarly, the hypoosmolarity-induced current is inhibited from 37.4 ± 4.7 pA/pF to 5.6 ± 2.1 pA/pF by 30 μM DCPIB (n = 4 mice, **P < 0.001). Both currents quickly recover following the wash out of DCPIB. (B) RT PCR and Western blots show relative mRNA (normalized to the expression level in spleen) and protein expression of LRRC8A in a variety of tissues (n = 4 mice) and the absence of LRRC8 protein in HEK293 KO cells. (C) The sequences targeted by shRNA-1 (red) and shRNA2 (green) against LRRC8A. The sequences of human (h) and mouse (m) LRRC8A listed show 100% homology. (D) Cre recombinase–mediated LRRC8A excision in nodose neurons from floxed mice reduces the pHo-conditioned VRAC current density (Id pA/pF) from14.9 ± 3.4 (GFP transduced, n = 4 mice) to 2.4 ± 1.0 (Cre transduced, n = 6 mice, *P < 0.05) and the hypoosmolarity current from 28.1 ± 5.4 (GFP transduced, n = 2 mice) to 9.3 ± 4.4 pA/pF (Cre transduced, n = 3 mice, *P < 0.05). LRRC8A knock down (KD) in shRNA1-transduced neurons reduces responses to the pHo-conditioned currents from 21.2 ± 3.7 in WT control mice (Con, n = 7) to 9.2 ± 3.1 (KD, n = 7 mice; *P < 0.05), and those to hypoosmolarity from 25.6 ± 4.0 (Con, n = 5) to 13.9 ± 3.5 (KD, n = 3 mice; *P < 0.05). Corresponding values in control vs. shRNA2 transduced neurons are 14.0 ± 1.9 (Con, n = 3) vs. 1.4 ± 0.6 (KD, n = 3 mice; **P < 0.001) with pHo-conditioned current; and 23.4 ± 6.4 (Con, n = 3) vs. 3.5 ± 1.2 (KD, n = 3 mice; *P < 0.05) with hypoosmolarity. (E) The pHo-conditioned and hypoosmolarity-induced VRAC current densities are compared in nodose neurons vs. DRG neurons and HEK293 cells. Although all 3 groups respond to hypoosmolarity (19.7 ± 5.1 for HEK293, n = 2; 17.5 ± 4.6 for DRG, n = 5 mice; and 25.1 ± 5.8 pA/pF for nodose, n = 5 mice), the pHo-conditioned current is seen predominantly in nodose neurons (18.8 ± 4.6, n = 5 mice) and minimally (**P < 0.01) in DRG (3.6 ± 1.7, n = 5mice) and HEK293 cells (2.1 ± 0.6 pA/pF, n = 2mice). All symbols within bars indicate individual neurons. Statistical comparisons of all means ± SE unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test.