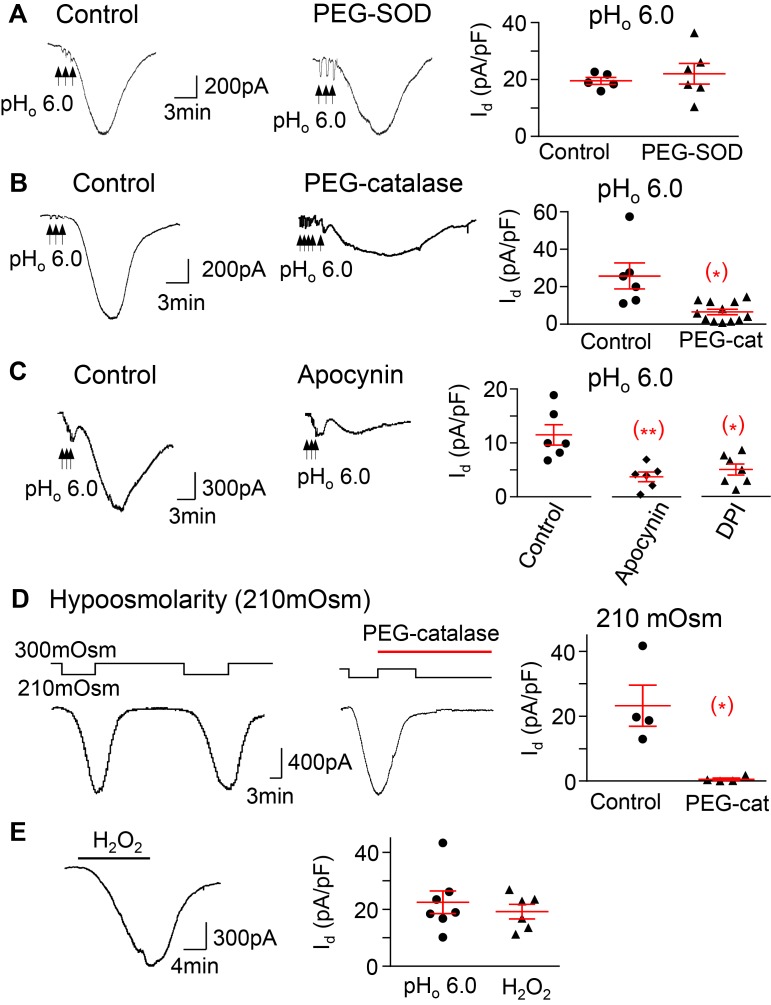
Figure 6. The pHo-conditioned Cl– current and VRAC are mediated by H2O2 and NADPH oxidase activation.
(A) The pHo-conditioned current is not blocked by a 30-minute application of 300 U/ml of the membrane permeable superoxide dismutase–polyethylene glycol (PEG-SOD) (20 ± 5 in control neurons, n = 3 mice, vs. 23 ± 5 pA/pF in neurons treated with SOD, n = 3 mice); (B) the current is blocked by 1,000 U/ml of the membrane permeable PEG-catalase (25.7 ± 6.9 in control neurons vs. 6.5 ± 1.5 pA/pF in neurons pretreated with catalase; n = 4 mice,*P < 0.05); and (C) the current is blocked in neurons pretreated with the inhibitors of NADPH oxidase apocynin (300 μM) and DPI (30 μM) (11.5 ± 1.9, n = 3 mice, in control vs. 3.7 ±0.l9, n = 3 mice, with apocynin,**P < 0.01, and vs. 5.0 ± 1.0 pA/pF, n = 3 mice, with DPI,*P < 0.05). (D) The current induced by hypoosmolarity (210 mOsm) is also blocked after exposure to PEG catalase (1,000 U/ml) (23.3 ± 6.3 vs. 0.6 ± 0.4 pA/pF before and after catalase, n = 2 mice,*P < 0.05). (E) H2O2 (1 mM) induces a current (19.2 ± 2.5 pA/pF, n = 3 mice) that is similar to both the pHo-conditioned (22.4 ± 4.0 pA/pF, n = 4 mice) and hypoosmolarity-induced currents, as in D. The panels represent responses of individual neurons and the means ± SE of each group. Unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test, except for D, where the analysis was paired.