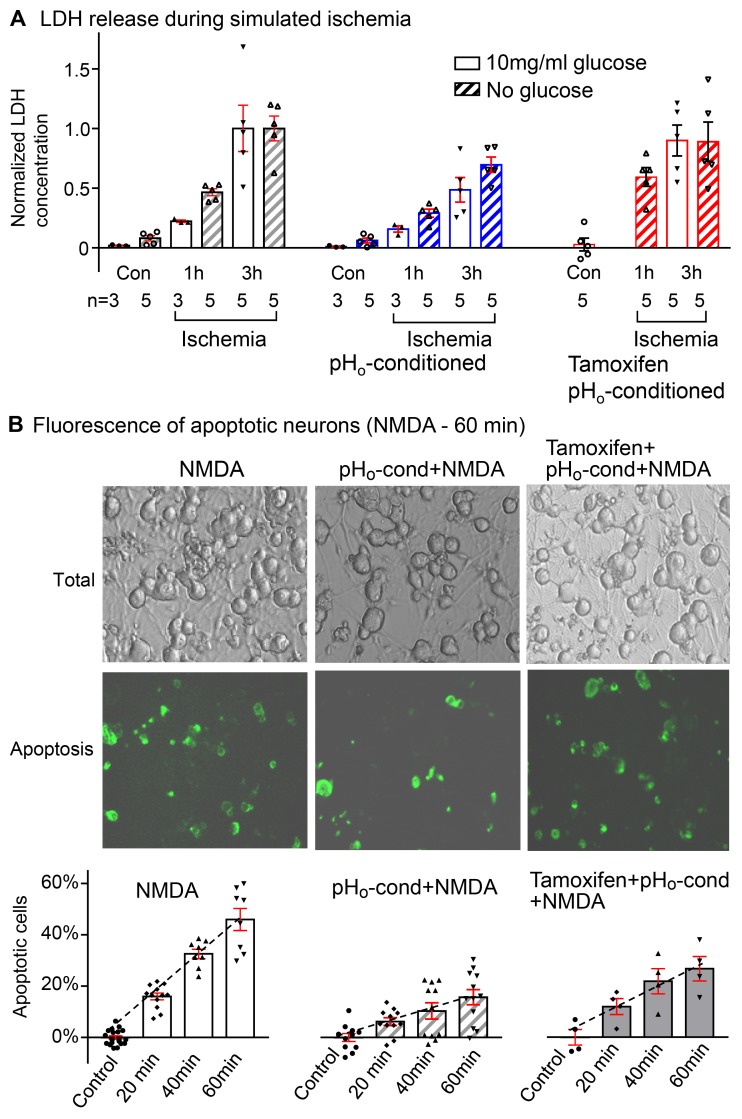
Figure 8. Protective effect of pHo-conditioned Cl– current during simulated ischemia and NMDA-induced apoptosis.
(A) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release from neurons in culture over a period of 1 and 3 hours exposure to “simulated ischemia” with acidic bathing solutions (pHo 5.0) that were oxygen deprived with glucose (open bars) or without glucose (striped bars). All responses are normalized to the mean value obtained after 3 hours of ischemia in each group (n = number of coverslips in each group). In each panel, control (Con) values were obtained over a period of 3 hours without ischemia and with or without glucose. The increase in LDH is negligible. The left panel shows progressive increases in LDH from 0.02 ± 0.01 to 0.22 ± 0.01 and 1.00 ± 0.19 at 1 and 3 hours of ischemia with glucose and from 0.08 ± 0.02 to 0.46 ± 0.03 and 1.00 ± 0.10 at 1 and 3 hours of ischemia without glucose. Activation of the low pHo–conditioned current (middle panel) reduces LDH release to corresponding values of 0.16 ± 0.03 and 0.48 ± 0.10 with glucose, and 0.29 ± 0.03 and 0.69 ± 0.06 without glucose, at 1 and 3 hours of ischemia, respectively; P < 0.05. When tamoxifen was added to prevent pHo conditioning (right panel), the protective effect is totally abrogated, and LDH release during “ischemia” was restored to 0.90 ± 0.13 at 3 hours with glucose and to 0.59 ± 0.08 and 0.89 ± 0.17 at 1 and 3 hour without glucose. (B) Neuronal apoptosis following NMDA exposure. The images show bright fields of all neurons on individual cover slips and the corresponding green fluorescent images of the apoptotic cells labeled with annexin V. In the absence of NMDA, there was essentially no detectable apoptosis over a period of 60 minutes (control). The percentile of apoptotic cells increased progressively to 15.9% ± 1.3% (n = 12), 32.6% ± 1.7% (n = 8), and 46.0% ± 4.3% (n = 8) after exposures to NMDA for 20, 40, and 60 minutes (left panel). Following activation of the Cl– current (middle panel), the % apoptotic cells is reduced dramatically to 6.2% ± 1.5% (n = 11), 10.3% ± 3.2% (n = 11), and 15.6% ± 3.1% (n = 12), respectively (P < 0.01). Tamoxifen (10 μM) partially reversed the protective effect of low pHo conditioning (right panel), and apoptosis increased to 11.9% ± 3.1% (n = 4), 21.6% ± 4.9% (n = 4), and 26.5% ± 1.5% (n = 4) for 20, 40, and 60 minutes NMDA exposure (P < 0.01). Bars include responses of individual coverslips with means ± SE; all statistical comparisons used 2-way ANOVA.