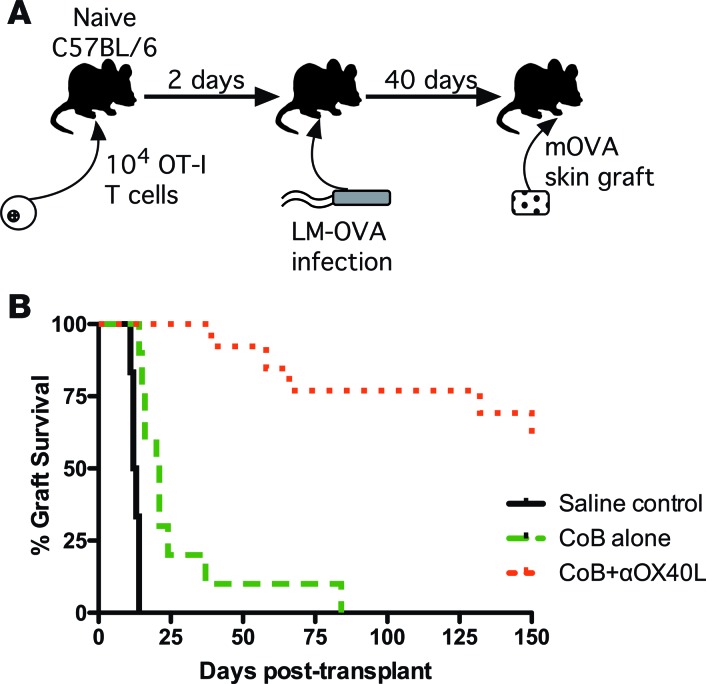
Figure 4. Disruption of OX40L signaling pathway prevents costimulation blockade–resistant rejection by memory alloreactive T cells.
(A) Schematic of donor-specific memory alloresponse transplant system. Ovalbumin-specific OT-I cells are adoptively transferred into naive C57BL/6 recipients, which are then infected with modified Listeria monocytogenes that produce the ovalbumin peptide (LM-OVA) to generate memory OT-I cells. Thirty days after infection, the recipients are rechallenged with skin grafts from mice ubiquitously expressing membrane-bound ovalbumin (mOVA). (B) mOVA skin graft recipients with donor-specific memory T cells show improved survival when treated with combined costimulation blockade (CoB) + anti-OX40L compared with treatment with CoB alone (n = 6–13 mice per group, P < 0.0001 by log-rank Mantel-Cox test).