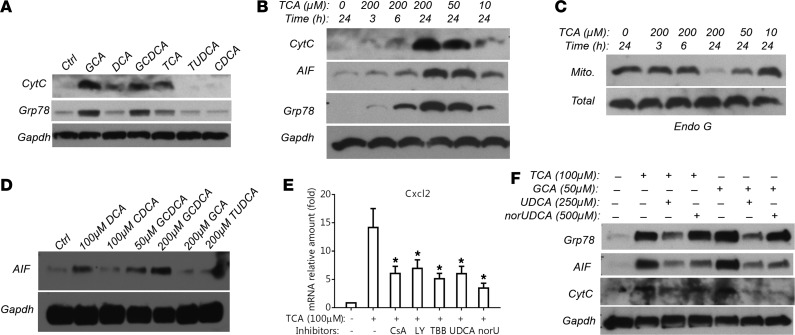
Figure 5. Bile acids induce hepatocyte mitochondrial injury and ER stress.
(A) Representative Western blot detecting leakage of mitochondrial protein cytochrome c (CytC) and ER protein Grp78 into the cytosol in mouse hepatocytes after a 24-hour treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA, 50 μM), glycocholic acid (GCA, 200 μM), glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA, 200 μM), deoxycholic acid (DCA, 50 μM), taurocholic acid (TCA, 200 μM), and tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA, 200 μM). (B) Representative Western blot demonstrating that TCA treatment released CytC, apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF, a mitochondria-specific protein), and Grp78 from mitochondria and the ER into the cytosol in a dose- and time-dependent manner in mouse hepatocytes. (C) Representative Western blot showing reduction of mitochondrial (Mito) but not total cellular endonuclease G (Endo G) protein expression in TCA-treated mouse hepatocytes (dose and time dependency). (D) Western blot detection of GCDCA treatment (24 hours) resulting in AIF leaking into the cytosol in human hepatocytes. (E) TCA (100 μM) induction of Cxcl2 mRNA expression in mouse hepatocytes was significantly reduced by cyclosporin A (CsA, 3 μM), LY294002 (LY, 40 μM), 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole (TBB, 25 μM), ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA, 250 μM), and norUDCA (norU, 500 μM). Cells were treated for 24 hours (mean ± SD, n ≥ 4). *P < 0.05 vs. TCA treatment alone by 1-way ANOVA. (F) UDCA and norUDCA treatment reduced bile acid–induced leakage of AIF and Grp78 protein into cytosol in mouse hepatocytes. All Western blots shown here have been repeated in at least 3 independent experiments.