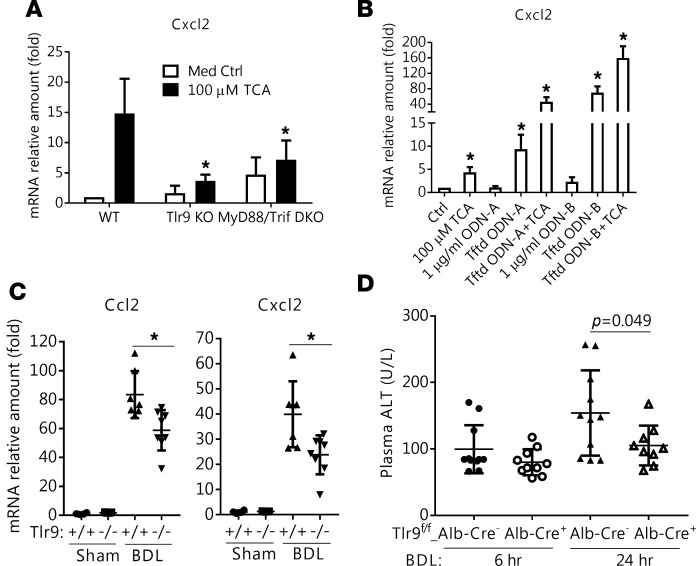
Figure 6. Tlr9 is involved in bile acid induction of Cxcl2 in vitro in mouse hepatocytes and in vivo in BDL mouse liver.
(A) Taurocholic acid (TCA, 100 μM) stimulation of Cxcl2 mRNA expression was significantly decreased in hepatocytes from Tlr9 knockout (KO) and MyD88/Trif double-knockout (DKO) mice when compared with hepatocytes from WT mice. Cells were treated for 24 hours, and results are the mean ± SD, *P < 0.05 vs. WT TCA treatment, n ≥ 4. (B) Transfected (Tftd) Tlr9 agonists (ODN-A and ODN-B, 1 μg/ml) showed synergistic effects with TCA (100 μM) in stimulation of Cxcl2 mRNA expression in mouse hepatocytes. Sixteen hours after transfection, cells were treated with TCA for 6 hours (mean ± SD, n ≥ 3). The control cells were treated with transfection medium, and their Cxcl2 expression was set to 1. (C) Ccl2 and Cxcl2 liver mRNA expression was significantly lower in Tlr9 whole-body KO mice than in WT mice after 7 days of bile duct ligation (BDL). Results are the mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, n = 6–7. (D) Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) serum levels were significantly reduced in hepatocyte-specific Tlr9 KO (Tlr9fl/fl-Alb-Cre+) mice 24 hours, but not 6 hours, after BDL. P values determined by 2-tailed Student’s t test.