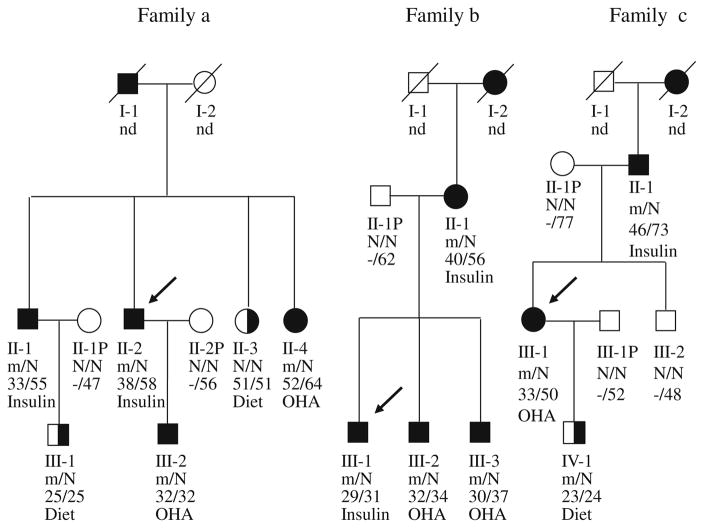
Fig. 4.
Pedigrees, genotypes and clinical characteristics of families a, b and c. Black circles and squares indicate participants diagnosed with type 2 diabetes; half-filled black circles and squares indicate IGT; white circles and squares indicate normal glucose tolerance (NGT); black arrows indicate the index cases for the three families. Individuals treated with insulin did not undergo the OGTT. The numbers under the symbols are the family members′ identification numbers, followed below by the genotype at codon 27 in family a, codon 192 in family b and codon 116–117 in family c, then age at diabetes diagnosis for affected members and age at examination, followed by treatment for diabetes. nd, not determined. Family a, Pedigree and genotypes of family a. Left pedigree shows the segregation of the R27H mutation. For the genotype, N shows normal allele (Arg); m shows mutant allele (His) at codon 27. The parametric LOD score for this pedigree was 0.83. OHA, oral hypoglycaemic agents, gliclazide. Family b, Pedigree and genotypes of family b. Middle pedigree shows the segregation of the R192H mutation. For the genotype, N shows normal allele (Arg); m shows mutant allele (His) at codon 192. The parametric log10 of odds (LOD) score for this pedigree was 0.60. OHA, glimepiride. Family c, Pedigree and genotypes of family c. Right pedigree shows the segregation of the S116F117del mutation. N shows normal allele S116F117; m shows mutant allele S116F117del (His) at codon116-117. The parametric LOD score for this pedigree was 0.52. OHA, gliclazide