Abstract
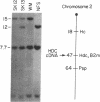
Histamine is a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and an important modulator of gastric acid secretion, vasomotor control, inflammation, and allergic reactions. In biological systems the formation of histamine from its precursor histidine is catalyzed by the enzyme L-histidine decarboxylase (HDC; L-histidine carboxy-lyase, EC 4.1.1.22). We have cloned HDC-encoding cDNA from a fetal rat liver cDNA library (phage lambda gt11) have deduced the amino acid sequence from the nucleotide sequence. The clone was proven to be HDC cDNA by expression of active recombinant enzyme in COS cells and by chromosomal mapping. The cDNA encodes a protein of Mr 73,450 (655 amino acid residues). The discrepancy between this molecular weight and the size of the purified fetal liver protein subunits [Taguchi, Y., Watanabe, T., Kubota, H., Hayashi, H. & Wada, H. (1984) J. Biol. Chem. 259, 5214-5221] (Mr = 54,000) suggests that HDC may be posttranslationally processed. The 469 amino acid residues from the amino-terminal portion of the protein share 50% identity with rat and Drosophila L-dopa decarboxylases and much less homology with other characterized amino acid decarboxylases.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans R. J., Denis K. A., Taylor A., Wall R. Expression of an immunoglobulin heavy chain gene transfected into lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1292–1296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eveleth D. D., Gietz R. D., Spencer C. A., Nargang F. E., Hodgetts R. B., Marsh J. L. Sequence and structure of the dopa decarboxylase gene of Drosophila: evidence for novel RNA splicing variants. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2663–2672. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., May J. M. In vitro phosphorylation of a synthetic collagen peptide by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Coll Relat Res. 1984 Jan;4(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegstrand L. R. A direct, sensitive microassay for mammalian histidine decarboxylase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 15;34(20):3711–3716. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90235-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., Halden N. F., Buckler C. E., Kozak C. A. Genetic mapping of the mouse c-fms proto-oncogene to chromosome 18. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1055–1056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1055-1056.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszti Z., Magyar K. Regulation of histidine decarboxylase activity in rat hypothalamus in vitro by ATP and cyclic AMP: enzyme inactivation under phosphorylating conditions. Agents Actions. 1984 Apr;14(3-4):546–549. doi: 10.1007/BF01973868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh Q. K., Snell E. E. Histidine decarboxylase of Lactobacillus 30a. Hydroxylamine cleavage of the -seryl-seryl- bond at the activation site of prohistidine decarboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1521–1524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh Q. K., Snell E. E. Pyruvoyl-dependent histidine decarboxylases. Preparation and amino acid sequences of the beta chains of histidine decarboxylase from Clostridium perfringens and Lactobacillus buchneri. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2798–2803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph D. R., Hall S. H., French F. S. Identification of complementary DNA clones that encode rat androgen binding protein. J Androl. 1985 Nov-Dec;6(6):392–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1939-4640.1985.tb03301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph D. R., Hall S. H., French F. S. Rat androgen-binding protein: evidence for identical subunits and amino acid sequence homology with human sex hormone-binding globulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahana C., Nathans D. Nucleotide sequence of murine ornithine decarboxylase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1673–1677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Kaufman D. L., Tobin A. J. Glutamic acid decarboxylase cDNA: nucleotide sequence encoding an enzymatically active fusion protein. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2768–2772. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02768.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. A., Bulfield G. A structural gene (Hdc-s) for mouse kidney histidine decarboxylase. Biochem Genet. 1984 Aug;22(7-8):645–656. doi: 10.1007/BF00485850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. A., Johnson W. A., Hirsh J. Regulated splicing produces different forms of dopa decarboxylase in the central nervous system and hypoderm of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3335–3342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr, Roskoski L. M. A rapid histidine decarboxylase assay. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90599-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savany A., Cronenberger L. Properties of histidine decarboxylase from rat gastric mucosa. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):593–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi Y., Watanabe T., Kubota H., Hayashi H., Wada H. Purification of histidine decarboxylase from the liver of fetal rats and its immunochemical and immunohistochemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5214–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi Y., Watanabe T., Shiosaka S., Tohyama M., Wada H. Immunohistochemical analysis of the cross-reaction of anti-rat histidine decarboxylase antibody with guinea-pig DOPA decarboxylase. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 12;340(2):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90919-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Horio Y., Taketoshi M., Imamura I., Ando-Yamamoto M., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Kuroda M., Wada H. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA of rat dopa decarboxylase: partial amino acid homologies with other enzymes synthesizing catecholamines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8142–8146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanase S., Kojima H., Morino Y. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate binding site of pig heart alanine aminotransferase. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):3002–3007. doi: 10.1021/bi00581a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo A., Sabriá J., Rodriguez R., Brandner R., Rodriguez J., Palacios J. M., Blanco I. Properties and ontogenic development of membrane-bound histidine decarboxylase from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1988 Nov;51(5):1400–1406. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaaler G. L., Brasch M. A., Snell E. E. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent histidine decarboxylase. Nucleotide sequence of the hdc gene and the corresponding amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11010–11014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderslice P., Copeland W. C., Robertus J. D. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of wild type and a mutant histidine decarboxylase from Lactobacillus 30a. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15186–15191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Taguchi Y., Shiosaka S., Tanaka J., Kubota H., Terano Y., Tohyama M., Wada H. Distribution of the histaminergic neuron system in the central nervous system of rats; a fluorescent immunohistochemical analysis with histidine decarboxylase as a marker. Brain Res. 1984 Mar 12;295(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90811-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Watanabe T., Harino S., Fukui H., Wada H. The effects of protease inhibitors on histidine decarboxylase activities and assay of enzyme in various rat tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct;615(2):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90511-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]