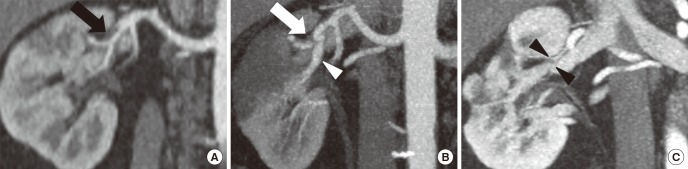
Fig. 2.
MDCT images in 49-year-old man with new-onset hypertension. (A) Initial. (B) One-month follow-up. (C) 26-month follow-up. Initial curved MPR image (A) shows that the true lumen of a segmental renal artery is compressed by a thrombosed false lumen (black arrow). Curved MPR image at 1-month follow-up (B) shows the aggravated narrowing of the true lumen (white arrow) and the aneurysmal change has developed (white arrow head). The previous infarction area has been atrophied in the cured MPR image at 26-month follow-up (C), even though the dissected renal vessels have been normalized (black arrow heads). Spontaneous renal artery dissection was diagnosed.
MDCT = multidetector computed tomography, MPR = multiplanar reconstruction.