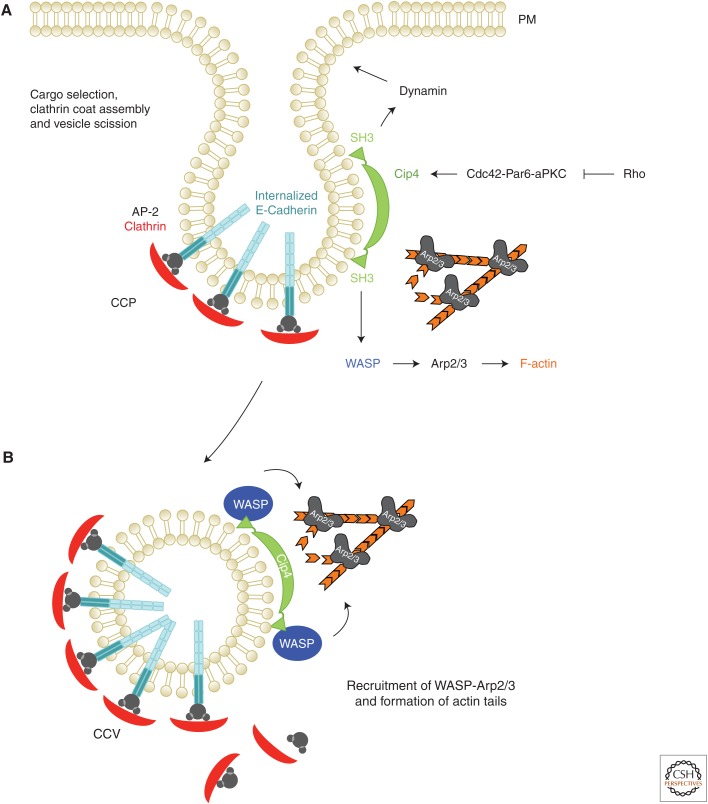
Figure 2.
The Cdc42-Par6-aPKC polarity complex promotes E-cadherin endocytosis by recruiting the Cip4-WASP-Arp2/3 actin machinery. (A) E-cadherin is actively internalized by clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Vertebrate E-cadherin contains an AP-2 binding motif. Once E-cadherin is selected and bound by AP-2 or other cargo-adapter proteins (e.g., Numb, see main text), the clathrin coat is assembled. Cdc42–Par6–aPKC recruits Cip4 to the site of E-cadherin endocytosis. F-BAR proteins such as Cip4 are thought to facilitate the scission by recruiting Dynamin to the neck of a nascent vesicle. This recruitment requires the SH3 domain that binds to Proline-rich motifs of Dynamin but also the Arp2/3 activator Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP). (B) WASP-Arp2/3-mediated actin polymerization has a supportive function in vesicle budding and promotes actin-comet-tail-based movement of newly formed clathrin-coated vesicles. The GTPase Rho seems to suppress cadherin endocytosis by antagonizing Cdc42–Par6–aPKC functions (Warner and Longmore 2009).